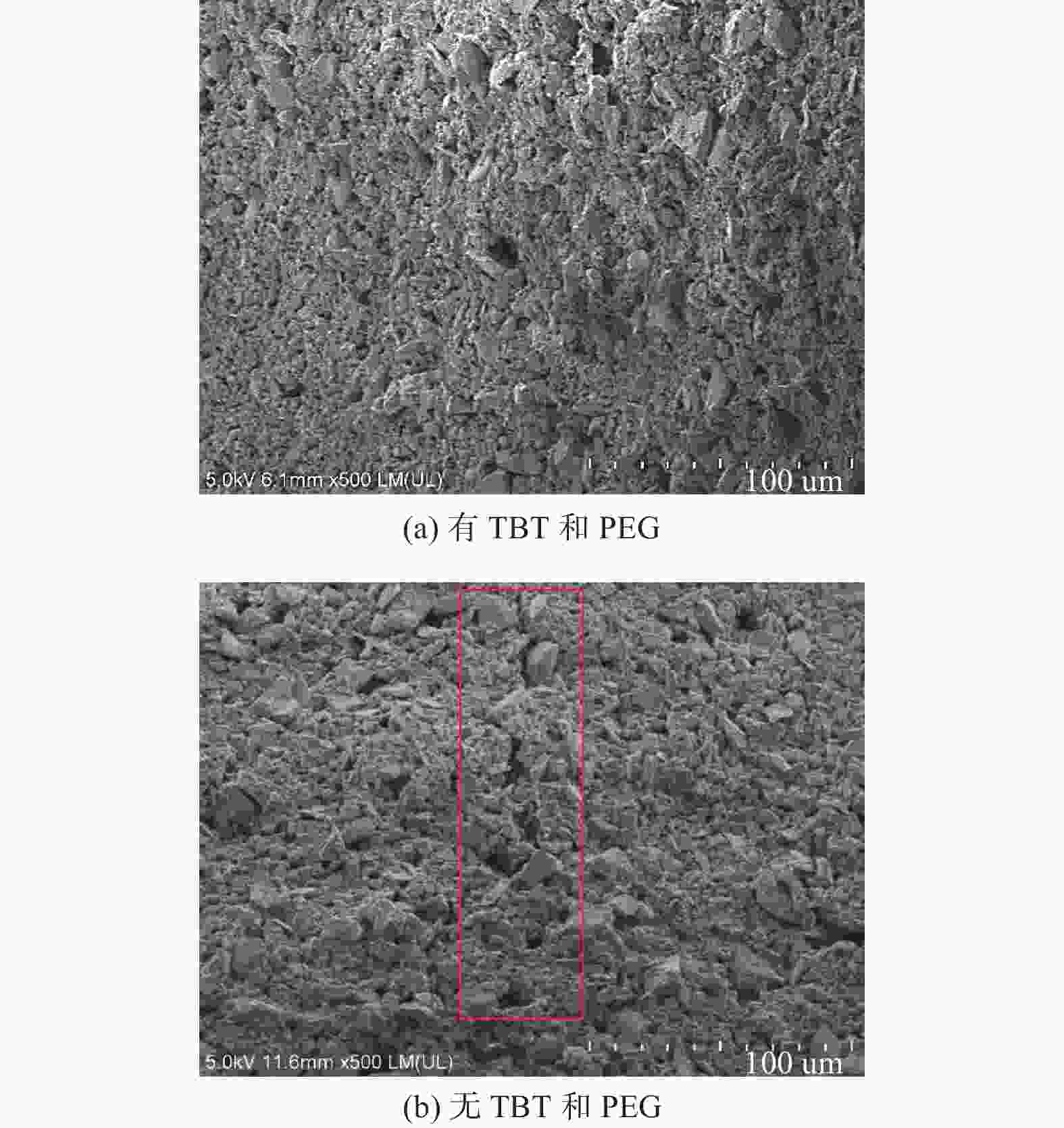
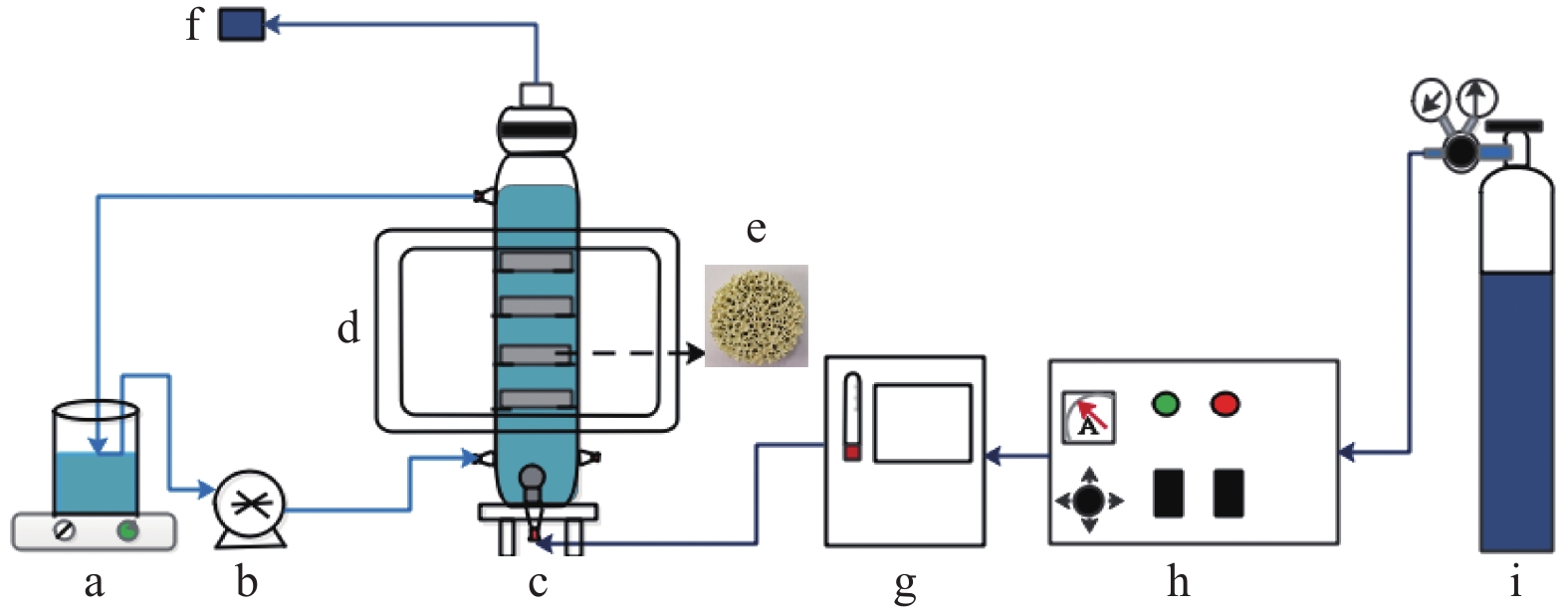
Preparation of photocatalytic ozonation SiC foam and its application in levofloxacin degradation
-
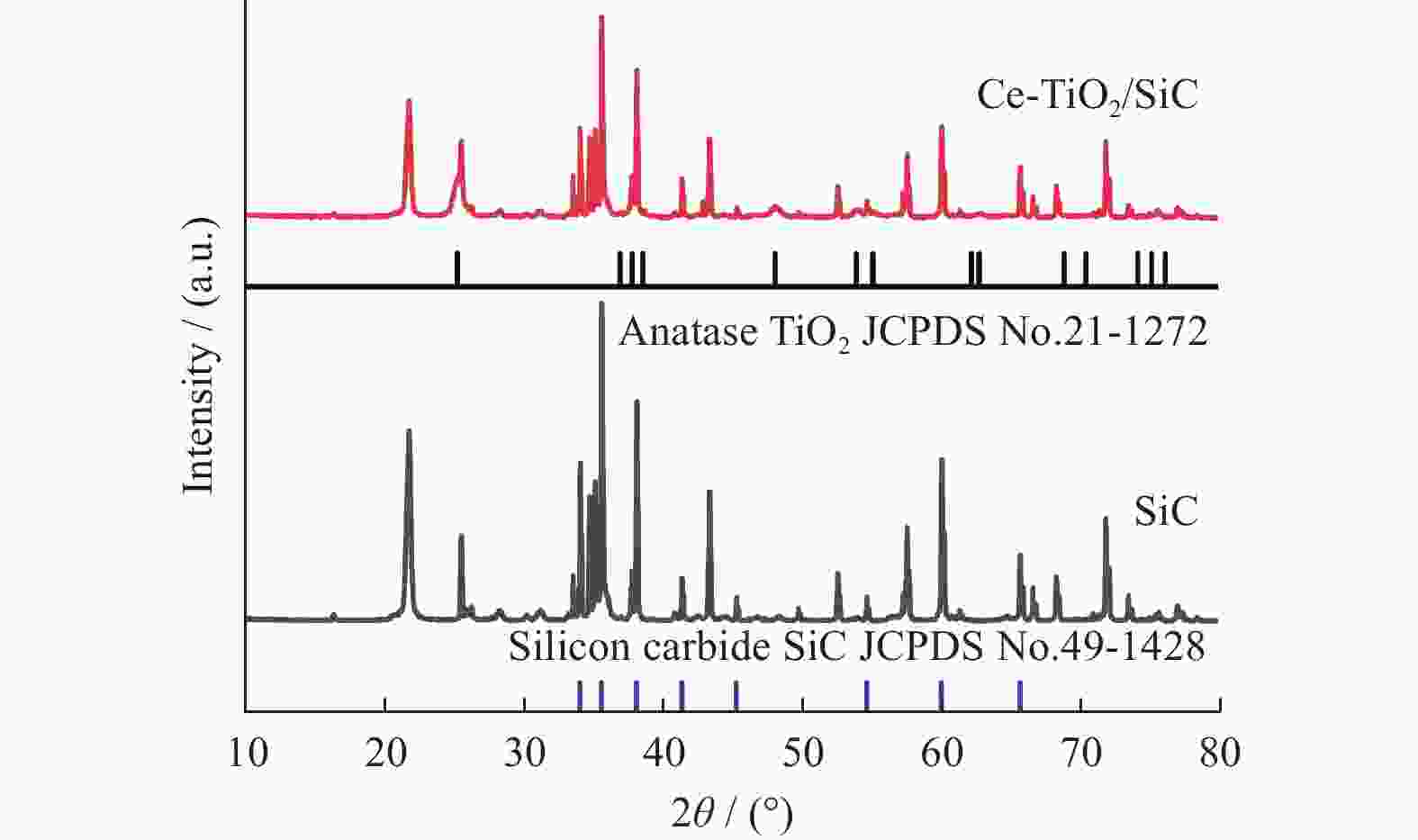
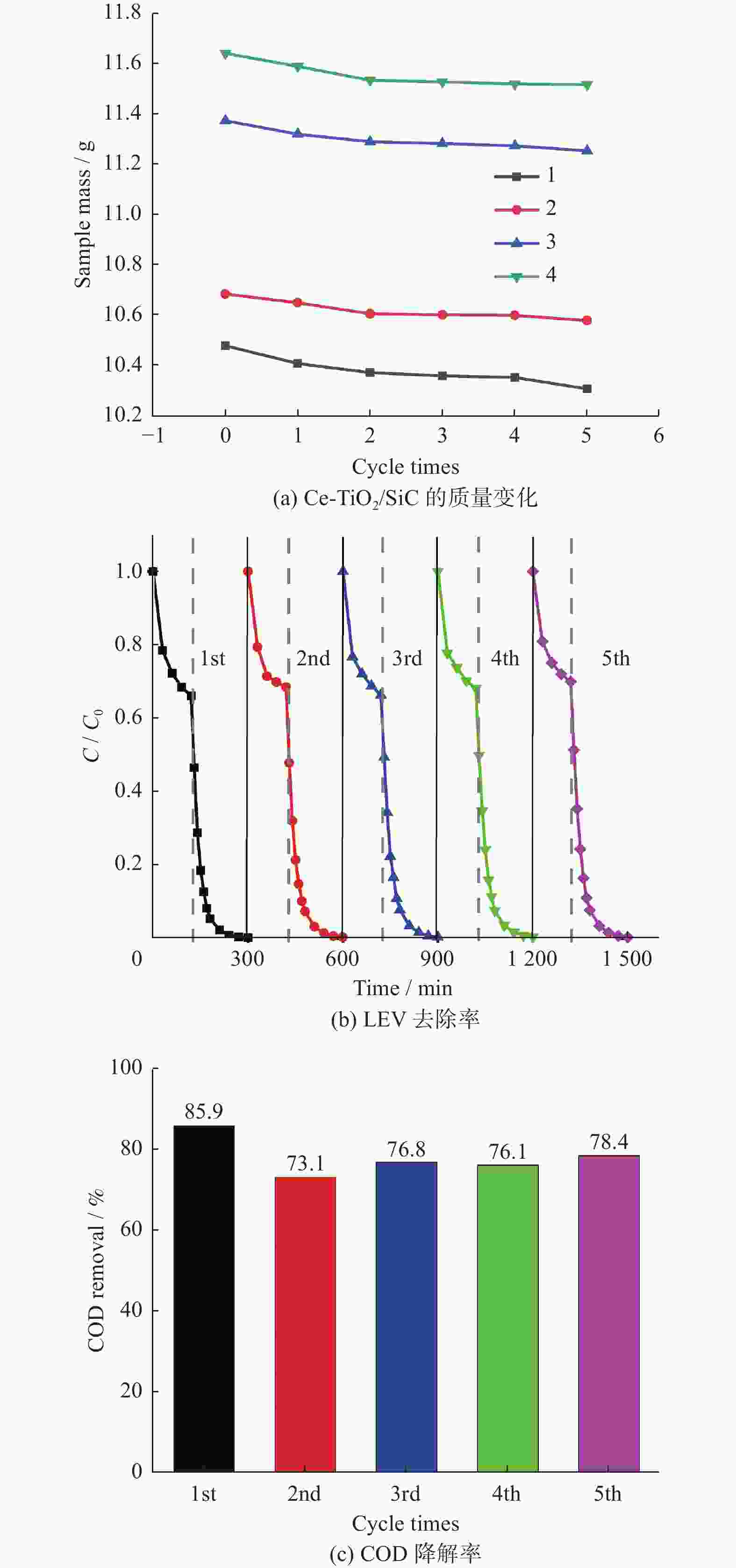
摘要: 针对抗生素难以降解而造成环境污染问题,以左氧氟沙星(Levofloxacin,LEV)为目标污染物,制备Ce-TiO2 /SiC泡沫陶瓷复合材料,并由此构建光催化臭氧氧化耦合体系(Ce-TiO2/SiC + LED + O3). 结果表明,该耦合体系能有效降解LEV,去除率为99%,化学需氧量(Chemical Oxygen Demand,COD)降解率高达85.9%. 该耦合体系体现了较高的协同效应,其一级反应动力学速率常数大于臭氧氧化(O3)与光催化(Ce-TiO2/SiC + LED)之和. 另外,Ce-TiO2 /SiC泡沫陶瓷的稳定性实验表明,在5次重复使用实验后,光催化臭氧氧化活性基本不变.Abstract: To solve the problem of environmental pollution caused by the difficult degradation of antibiotics, Ce-TiO2/SiC foam was prepared, levofloxacin (Levofloxacin, LEV) was chosen as the target pollutant, and a photocatalytic ozonation coupling system (Ce-TiO2/SiC + LED + O3) was studied. The results show that the coupling system can effectively degrade LEV, the LEV removal was 99% and the chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal was as high as 85.9%. The coupling system showed a good synergistic effect, and its first-order reaction kinetic rate constant was greater than the sum of ozonation (O3) and photocatalysis (Ce-TiO2/SiC + LED). In addition, the stability experiment of Ce-TiO2/SiC foam showed that the photocatalytic ozonation activity is basically unchanged after five reuses.
-
表 1 实验试剂
Table 1. Laboratory reagents
试剂名称 纯度 供应单位 无水乙醇 分析纯 ≥ 99.7% 上海泰坦科技股份有限公司 钛酸四丁酯 分析纯 99% 上海泰坦科技股份有限公司 六水合硝酸铈 分析纯 99% 上海泰坦科技股份有限公司 冰醋酸 分析纯 99% 上海泰坦科技股份有限公司 聚乙二醇 化学纯 国药集团化学试剂有限公司 左氧氟沙星 分析纯 ≥ 98.0% 阿拉丁试剂(上海)有限公司 COD检测试剂 — 北京连华科技有限公司 SiC泡沫陶瓷 — 铬晶新材料有限公司 表 2 不同降解方法降解LEV的比较总结
Table 2. Summary of comparison of different methods for degrading LEV
降解方法 LEV去除率/% kLEV × 10−2
/min−1R12 COD降解率/% kCOD × 10−3
/min−1R22 LED 2.6 0.02 0.9594 0 — — O3 98.7 2.54 0.9832 52.2 3.86 0.9732 (10%)Ce-TiO2/SiC + LED 53.1 0.20 0.9907 44.2 1.15 0.9709 (10%)Ce-TiO2/SiC + O3 99.6 2.98 0.9778 81.8 7.24 0.9311 (10%)Ce-TiO2/SiC + LED + O3 99.8 3.23 0.9857 85.9 8.44 0.9853 -
[1] 张万鹏, 郑立庆, 杨鑫雨, 等. 球磨−煅烧法制备Fe3O4-CuxO及其活化Oxone降解盐酸左氧氟沙星[J] . 中国环境科学,2020,40(1):143 − 152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.01.016 [2] LYU J, YANG L S, ZHANG L, et al. Antibiotics in soil and water in China: A systematic review and source analysis[J] . Environmental Pollution,2020,266:115147. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115147 [3] LI Z, LI M, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Antibiotics in aquatic environments of China: A review and meta-analysis[J] . Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2020,199:110668. [4] XIA Y J, DAI Q Z. Electrochemical degradation of antibiotic levofloxacin by PbO2 electrode: Kinetics, energy demands and reaction pathways[J] . Chemosphere,2018,205:215 − 222. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.103 [5] JOSHI S M, GOGATE P R. Treatment of landfill leachate using different configurations of ultrasonic reactors combined with advanced oxidation processes[J] . Separation and Purification Technology,2019,211:10 − 18. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2018.09.060 [6] 朱晓兵, 金灿, 李小松, 等. LED可见光下Au/TiO2光催化氧化甲醛表观动力学[J] . 化工学报,2017,68(S1):196 − 203. [7] BUYUKADA M. Removal, potential reaction pathways, and overall cost analysis of various pollution parameters and toxic odor compounds from the effluents of turkey processing plant using TiO2 assisted UV/O3 process[J] . Journal of Environmental Management,2019,248:109298. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109298 [8] LI Y H, CHENG S W, YUAN C S, et al. Removing volatile organic compounds in cooking fume by nano-sized TiO2 photocatalytic reaction combined with ozone oxidation technique[J] . Chemosphere,2018,208:808 − 817. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.035 [9] XIE Y B, YANG J, CHEN Y, et al. Promising application of SiC without co-catalyst in photocatalysis and ozone integrated process for aqueous organics degradation[J] . Catalysis Today,2018,315:223 − 229. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.01.013 [10] SUZUKI H, ARAKI S, YAMAMOTO H. Evaluation of advanced oxidation processes (AOP) using O3, UV, and TiO2 for the degradation of phenol in water[J] . Journal of Water Process Engineering,2015,7:54 − 60. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2015.04.011 [11] ZHU Q Y, WANG Y Q, WANG L X, et al. Solvent-free crystallization of ZSM-5 zeolite on SiC foam as a monolith catalyst for biofuel upgrading[J] . Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2020,41(7):1118 − 1124. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(20)63550-1 [12] M'BRA I C, GARCÍA-MUÑOZ P, DROGUI P, et al. Heterogeneous photodegradation of Pyrimethanil and its commercial formulation with TiO2 immobilized on SiC foams[J] . Journal of Photochemistry & Photobiology A:Chemistry,2019,368:1 − 6. [13] WANG Y P, KE L Y, PENG Y J, et al. Ex-situ catalytic fast pyrolysis of soapstock for aromatic oil over microwavedriven HZSM-5@SiC ceramic foam[J] . Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,402:126239. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126239 [14] TOUATI A, HAMMEDI T, NAJJARA W, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of textile wastewater in presence of hydrogen peroxide: Effect of cerium doping titania[J] . Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry,2016,35:36 − 44. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2015.12.008 [15] KONSTANTINOU I K, ALBANIS T A. TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: kinetic and mechanistic investigations: A review[J] . Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2004,49(1):1 − 14. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2003.11.010 [16] LING Y, LIAO G Z, XIE Y H, et al. Coupling photocatalysis with ozonation for enhanced degradation of atenolol by Ag-TiO2 micro-tube[J] . Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry,2016,329:280 − 286. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2016.07.007 -





 下载:
下载: