Dynamic modeling and analysis of flexure mechanism in two-dimensional micro motion stage
-
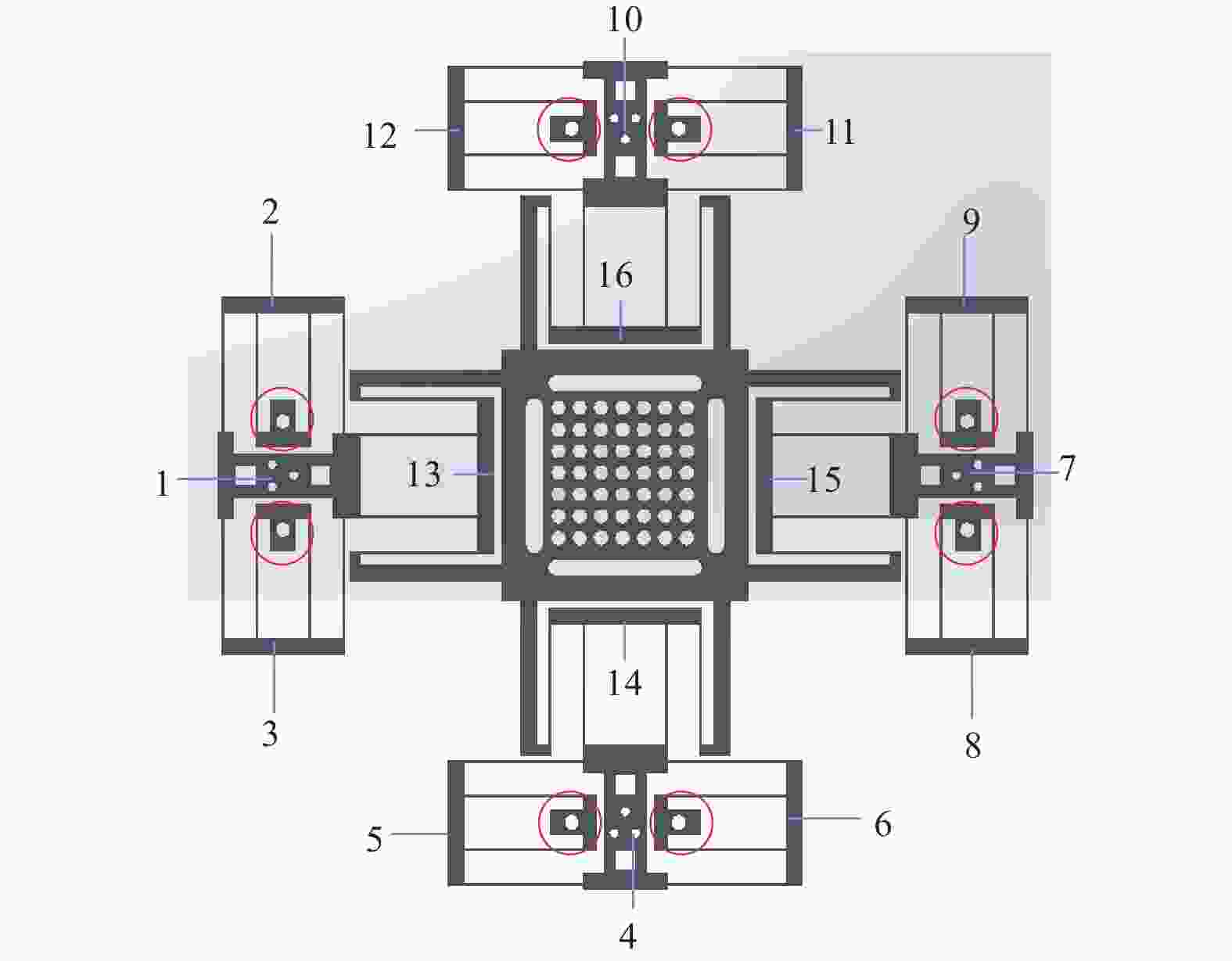
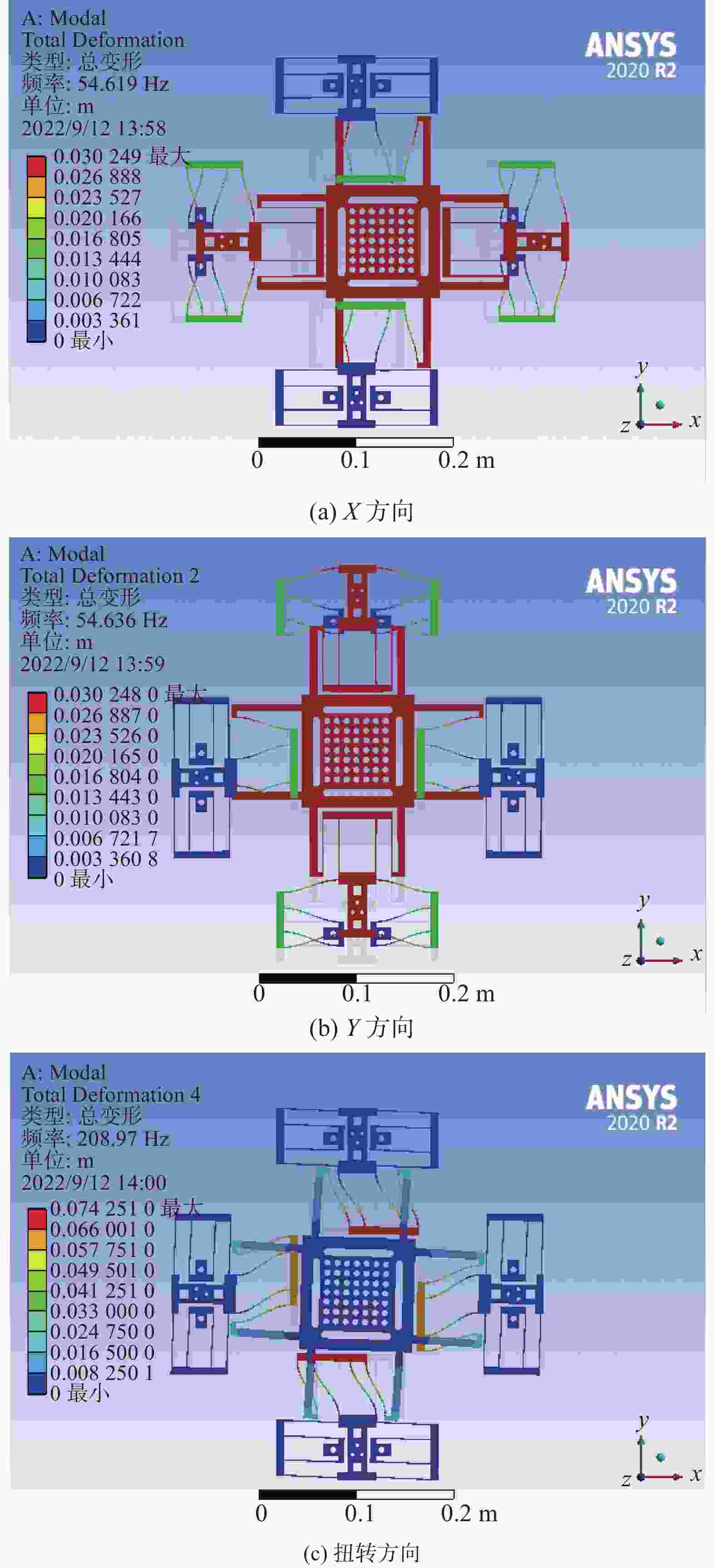
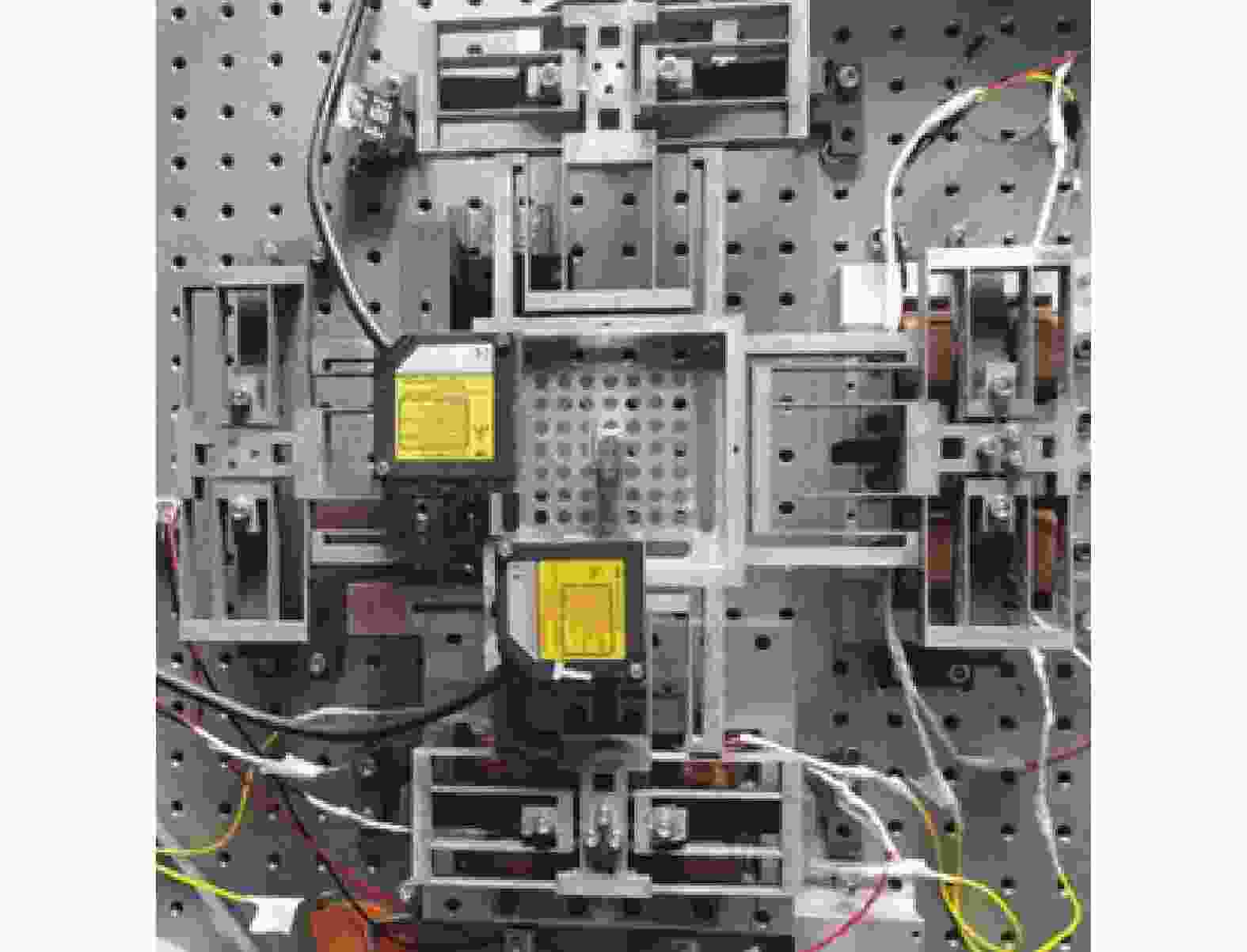
摘要: 提出一种基于并联柔性机构的两自由度平动解耦并联微动平台. 平台采用复合双平行四杆柔性机构模块,采用结构对称约束消除轴间耦合和寄生位移的产生,实现X,Y方向的平动. 采用刚度矩阵法对该并联柔性机构进行理论分析,根据观察法建立微动工作台的整体刚度矩阵,得到系统的运动微分方程,推导出系统各阶固有频率. 采用有限元分析法对微动工作台进行模态分析,得到微动工作台的固有频率和振型. 经过理论分析、有限元计算和试验测试,并对结果进行对比,结果的一致性说明理论分析的正确性和刚度矩阵分析的有效性.Abstract: A two degree of freedom translational decoupling parallel micropositioning stage based on parallel flexure mechanism was proposed. A compound double parallel four-bar flexure mechanism module was adopted in the stage, and structural symmetry constraints were introduced to eliminate the coupling between shafts and parasitic displacement, and translations in X and Y directions were achieved. The stiffness matrix method was used to analyze the parallel flexure mechanism in theory. According to the observation method, the overall stiffness matrix of the micropositioning stage was established, and the differential equations of motion of the system were obtained, and the natural frequencies of each order of the system were deduced. The modal analysis of the micropositioning stage was carried out by using the finite element method, and the natural frequency and mode shape of the micropositioning stage were obtained. Through theoretical analysis, finite element calculation and experimental test, the consistency of the results shows the correctness of theoretical analysis and the effectiveness of stiffness matrix analysis.
-
Key words:
- micropositioning /
- flexure mechanism /
- stiffness matrix /
- finite element
-
表 1 固有频率计算结果对比
Table 1. Comparison of natural frequency calculation results
模型 X方向模态/Hz Y方向模态/Hz 扭转频率/Hz 刚度矩阵模型 55.402 55.402 215.54 有限元模型 54.619 54.636 208.97 误差/% 1.434 1.402 3.144 -
[1] 杨维帆, 曹小涛, 张彬, 等. 空间望远镜次镜六自由度调整机构精密控制[J] . 红外与激光工程,2018,47(7):241 − 248. [2] ITO S, CIGARINI F, UNGER S, et al. Flexure design for precision positioning using low-stiffness actuators[J] . IFAC PAPERSONLINE,2016,49(21):200 − 205. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2016.10.548 [3] ITO S, TROPPMAIR S, LINDNER B, et al. Long-range fast nanopositioner using nonlinearities of hybrid reluctance actuator for energy efficiency[J] . IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2018,66(4):3051 − 3059. [4] LI Y M, XU Q S. A totally decoupled piezo-driven XYZ flexure parallel micropositioning stage for micro/nanomanipulation[J] . IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering,2010,8(2):265 − 279. [5] PINSKIER J, SHIRINZADEH B, CLARK L, et al. Development of a 4-DOF haptic micromanipulator utilizing a hybrid parallel-serial flexure mechanism[J] . Mechatronics,2018,50:55 − 68. doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2018.01.007 [6] 闫鹏, 李金银. 压电陶瓷驱动的长行程快刀伺服机构设计[J] . 光学精密工程,2020,28(2):390 − 397. [7] 韩慧, 刘丽. 大位移并联平面三自由度微定位平台设计[J] . 传感器与微系统,2021,40(6):3. doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2021)06-0073-03 [8] 周安泰. 基于多缺口型柔顺铰链的三自由度微动平台分析与设计[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2020. [9] 周睿, 周辉, 桂和利, 等. 基于柔性铰链的二自由度微动平台分析及优化[J] . 北京航空航天大学学报,2018,44(9):1982 − 1990. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0706 [10] ZHANG X, LAI L J, ZHANG L Q, et al. Hysteresis and magnetic flux leakage of long stroke micro/nanopositioning electromagnetic actuator based on Maxwell normal stress[J] . Precision Engineering,2022,75:1 − 11. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2022.01.003 -






 下载:
下载: