Supply chain return freight insurance and pricing strategy considering consumer risk avoidance
-
摘要: 针对线上买卖双方的退货运费承担纠纷,电商平台引入退货运费险来分摊商品退货风险,但宽松的退货政策又增加了消费者的退货行为。为此,将第三方保险公司引入制造商主导和网络零售商跟随的斯坦克尔伯格博弈中,考虑风险规避型消费者的退货行为和运费险敏感性,建立多方决策主体共同参与的卖家运费险、买家运费险和运费险共同分担等3种定价退货模型,研究网络零售商的定价决策和运费险策略。结果表明:消费者的风险规避态度有助于降低商品售价和运费险价格,提高市场需求和企业利润;运费险共同分担机制能够有效缓解客户流失;退货率较低时,消费者的运费险偏好有利于供应链总利润的增长。Abstract: In response to the return dispute between buyers and sellers in online transactions, e-commerce platforms have introduced return freight insurance to share the risk of product returns, but lenient return policies can also contribute to excessive returns. Thus, third-party insurance companies were incorporated into the Stackelberg game, which was dominated by the manufacturer and followed by the online retailer. Taking into account return behavior and freight insurance sensitivity of risk-averse consumers, three pricing return models with the participation of multiple decision makers, namely, the seller's freight insurance, the buyer's freight insurance and the shared freight insurance, were developed to analyze pricing decisions and freight insurance strategies of the online retailer. The results show that consumers’ risk aversion attitudes benefit to reduce the product price and freight insurance price, thereby increase market demand and profits for all members involved. The co-sharing mechanism for freight insurance can be effective in mitigating customer loss, and when the return rate is low, consumer preferences for return freight insurance are advantageous for the profitability of the overall supply chain.
-
Key words:
- supply chain management /
- return freight insurance /
- joint sharing /
- risk aversion
-
表 1 变量及参数说明
Table 1. Descriptions of variables and parameters
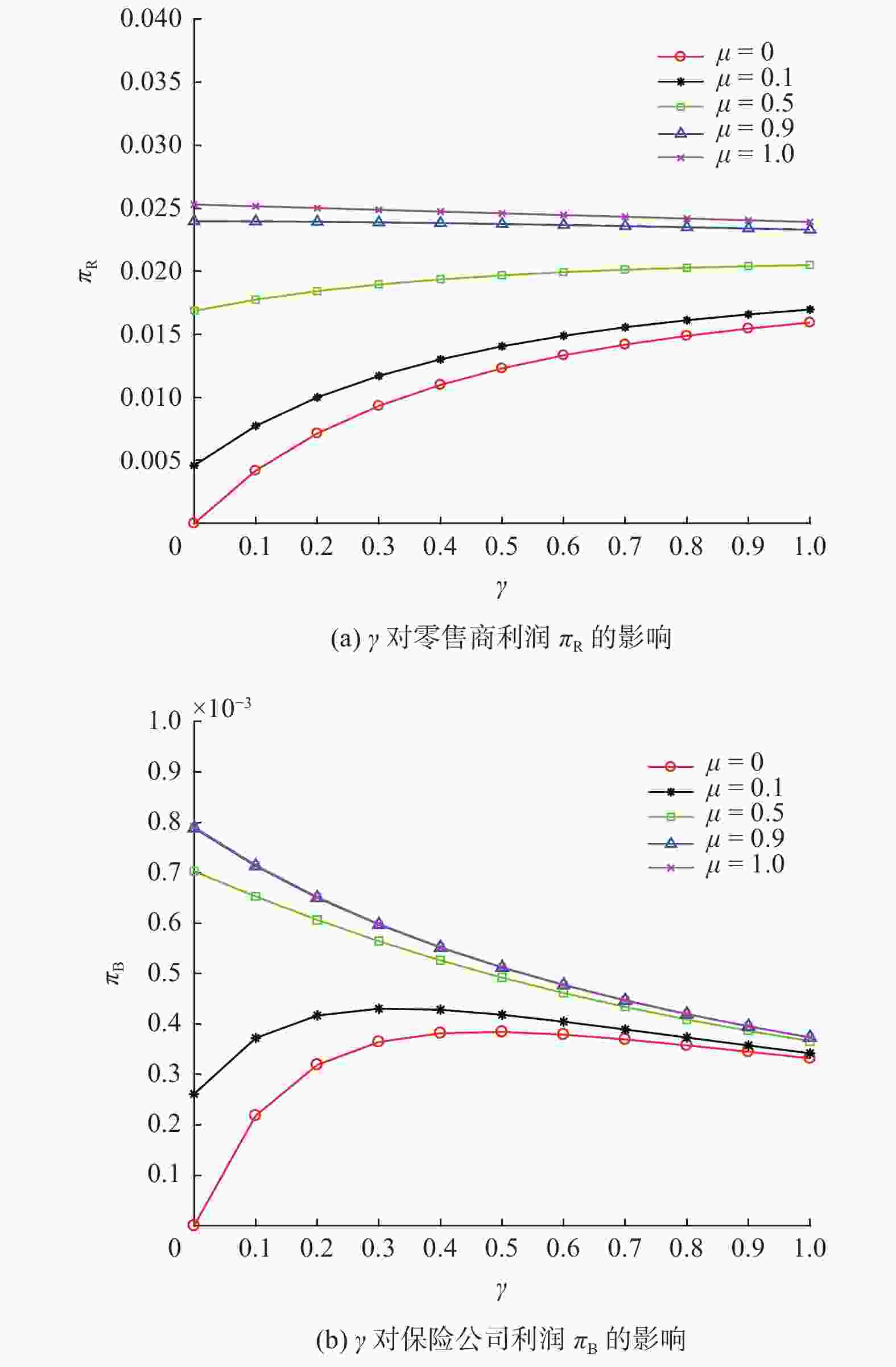
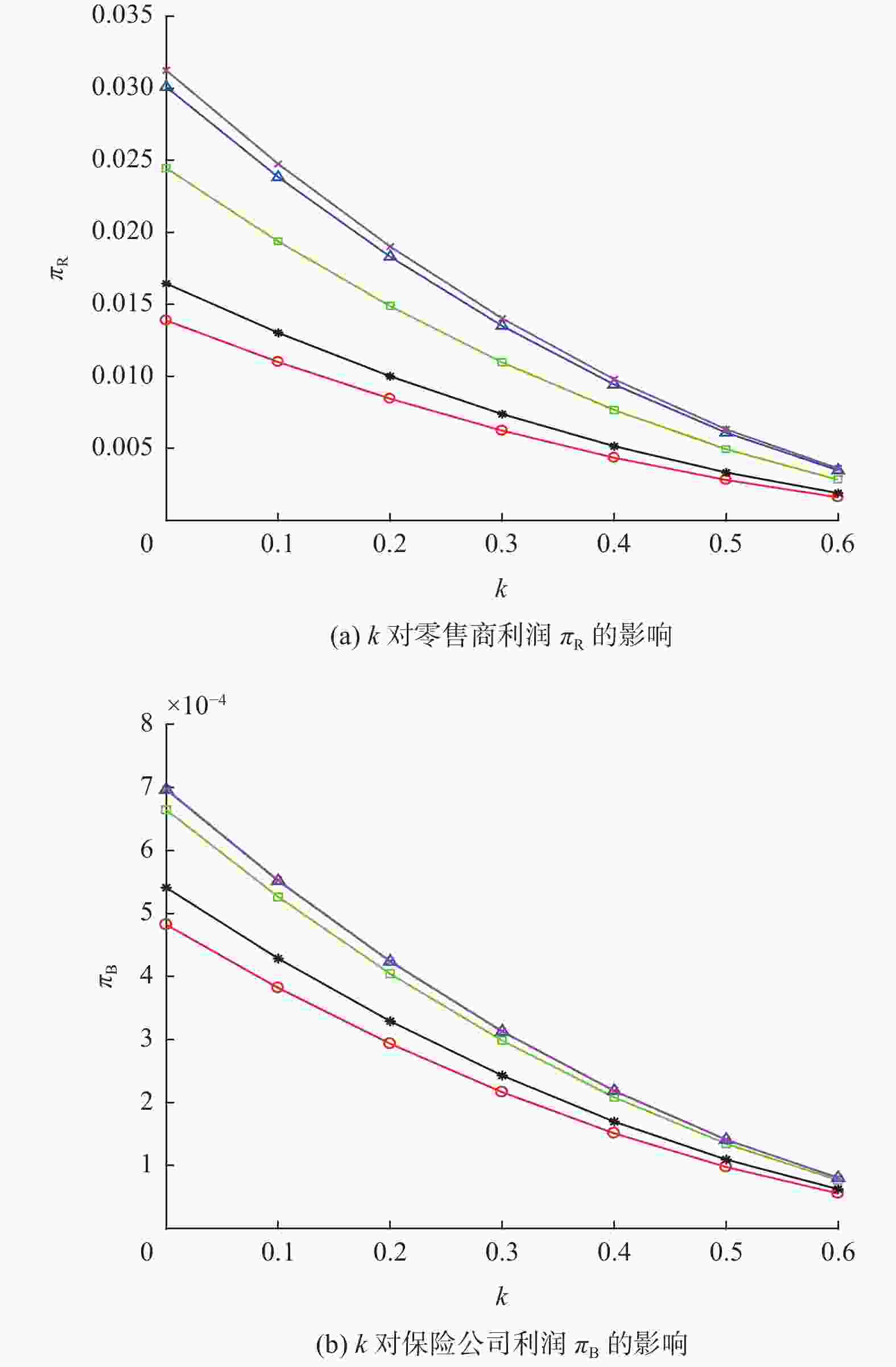
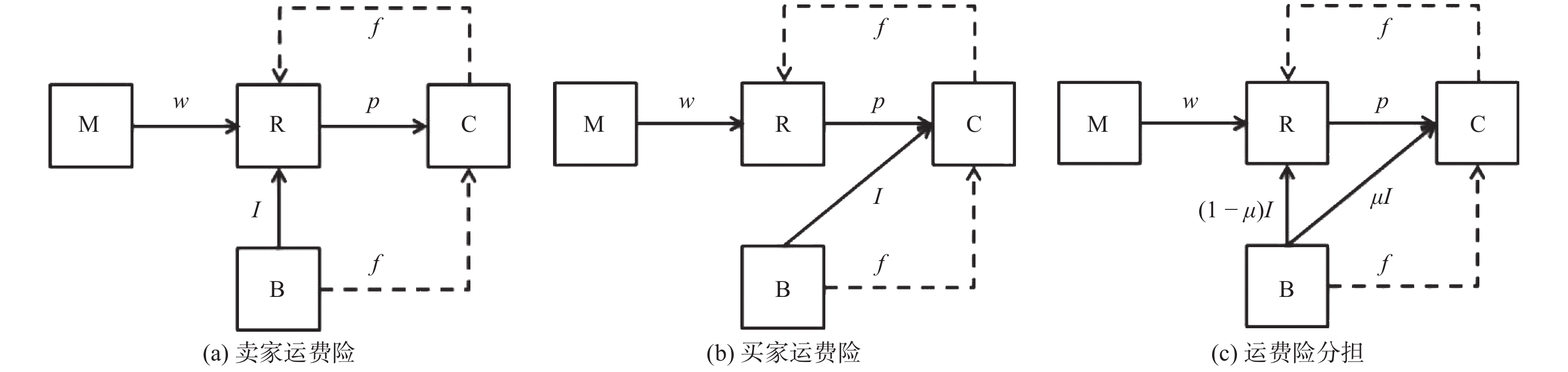
参数 含义 参数 含义 ${w_j}$ 制造商单位产品批发价格 $k$ 商品退货率 ${{\text{π}} _{ij}}$ 供应链成员的利润 $h$ 消费者退货麻烦成本 ${p_j}$ 零售商单位产品零售价格 $f$ 单位产品退货运费 $g$ 零售商单位商品的退货损失 $I$ 单位商品的退货运费险价格 $v$ 消费者对产品价值的估计 $\mu $ 消费者运费险价格分担比例 $U$ 消费者效用 $\gamma $ 消费者运费险价格敏感系数 注:下标$i = {\rm{M}},{\rm{R}},{\rm{B}}$;M为制造商;R为网络零售商;B为保险公司;下标$j = 1,2,3$;1为卖家运费险;2为买家运费险;3为运费险分担。 表 2 不同运费险策略的最优解
Table 2. The optimal solutions of different freight insurance policies
最优解 $ \mu = 0 $ $ \mu = 1 $ $ 0 < \mu < 1 $ ${w^*}$ $\dfrac{{1 - kh - kg - (\gamma + 1)kf}}{2}$ $\dfrac{{1 - kh - kg - (\gamma + 1)kf}}{2}$ $\dfrac{{1 - kh - kg - (\gamma + 1)kf}}{2}$ ${p^*}$ $ \dfrac{{(2 + 3\gamma )(1 - kh) + \gamma kg - (\gamma + 3{\gamma ^2})kf}}{{2(1 + 2\gamma )}} $ $\dfrac{{3 - 3kh + kg - (3 + 3\gamma )kf}}{4}$ $\dfrac{{(3\gamma + \mu + 2)(1 - kh) + (\gamma + \mu )(kg - (3\gamma + 2\mu + 1)kf)}}{{2(2\gamma + \mu + 1)}}$ ${I^*}$ $\dfrac{{1 - kh - kg + (3 + 7\gamma )kf}}{{4(1 + 2\gamma )}}$ $ \dfrac{{1 - kh - kg + (7 + 7\gamma )kf}}{{8(1 + \gamma )}} $ $\dfrac{{1 - kh - kg + (7\gamma + 4\mu + 3)kf}}{{4(2\gamma + \mu + 1)}}$ ${D^*}$ $\dfrac{{\gamma (1 - kh - kg - (\gamma + 1)kf)}}{{4(1 + 2\gamma )}}$ $\dfrac{{1 - kh - kg - (\gamma + 1)kf}}{8}$ $\dfrac{{(\gamma + \mu )(1 - kh - kg - (\gamma + 1)kf)}}{{4(2\gamma + \mu + 1)}}$ ${{\text{π}} _M}^*$ $ \dfrac{{\gamma {{(1 - kh - kg - (\gamma + 1)kf)}^2}}}{{8(1 + 2\gamma )}} $ $\dfrac{{{{(1 - kh - kg - (\gamma + 1)kf)}^2}}}{{16}}$ $\dfrac{{(\gamma + \mu ){{(1 - kh - kg - (\gamma + 1)kf)}^2}}}{{8(2\gamma + \mu + 1)}}$ ${{\text{π}} _R}^*$ $\dfrac{{\gamma {{(1 - kh - kg - (\gamma + 1)kf)}^2}}}{{16(1 + 2\gamma )}}$ $ \dfrac{{{{(1 - kh - kg - (\gamma + 1)kf)}^2}}}{{32}} $ $\dfrac{{(\gamma + \mu ){{(1 - kh - kg - (\gamma + 1)kf)}^2}}}{{16(2\gamma + \mu + 1)}}$ ${{\text{π}} _B}^*$ $\dfrac{{\gamma {{(1 - kh - kg - (\gamma + 1)kf)}^2}}}{{16{{(1 + 2\gamma )}^2}}}$ $\dfrac{{{{(1 - kh - kg - (\gamma + 1)kf)}^2}}}{{64(1 + \gamma )}}$ $\dfrac{{(\gamma + \mu ){{(1 - kh - kg - (\gamma + 1)kf)}^2}}}{{16{{(2\gamma + \mu + 1)}^2}}}$ -
[1] 张学龙, 吴豆豆, 王军进, 等. 考虑退货风险的制造商双渠道供应链定价决策研究[J] . 中国管理科学,2018,26(3):59 − 70. [2] 原逸超, 石岿然. 考虑策略型消费者和退货的零售商定价和订货决策研究[J] . 中国管理科学,2020,28(6):83 − 93. [3] 金亮, 郑本荣, 李志鹏. 基于顾客退货行为的在线零售商定价与体验渠道策略[J] . 管理评论,2022,34(1):168 − 179. [4] 刘健, 印蓉蓉, 杨朋辉, 等. 基于退货政策的双渠道零售商定价和策略研究[J] . 南京理工大学学报,2020,44(1):107 − 116. [5] LI G, LI L, SETHI S P, et al. Return strategy and pricing in a dual-channel supply chain[J] . International Journal of Production Economics,2019,215(9):153 − 164. [6] 王叶峰, 田中俊, 谢家平. 基于策略型消费者的预售退货策略研究[J] . 管理工程学报,2020,34(1):79 − 85. [7] LIU J, SUN X Y, LIU Y Y. Products pricing and return strategies for the dual channel retailers[J] . Operational Research,2022,22(4):3841 − 3867. doi: 10.1007/s12351-021-00670-1 [8] 王道平, 周玉, 葛根哈斯. 考虑参照价格效应和消费者行为的预售及退货策略[J] . 控制与决策,2021,36(11):2783 − 2793. [9] 孙军, 孙亮. 基于无缺陷退货的在线零售商运费承担策略研究[J] . 软科学,2014,28(6):41 − 45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8409.2014.06.009 [10] 赵晓敏, 胡淑慧. 网购环境下在线零售商的退货运费承担策略研究[J] . 中国管理科学,2019,27(1):53 − 62. [11] 杨雷, 常娜. 考虑退货运费险情况下的供应链运作决策研究[J] . 系统工程学报,2018,33(1):116 − 124. [12] 何莹莹, 郭春香. 预售模式下基于策略型消费者退货行为的运费险决策研究[J] . 管理学报,2018,15(8):1249 − 1255. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-884x.2018.08.018 [13] LIN J X, ZHANG J L, CHENG T C E. Optimal pricing and return policy and the value of freight insurance for a retailer facing heterogeneous consumers with uncertain product values[J] . International Journal of Production Economics,2020,229(11):1 − 18. [14] 胡振华, 舒行钢. 线上销售渠道下平台零售商的退货策略选择研究[J] . 湖南大学学报(社会科学版),2021,35(2):45 − 56. -





 下载:
下载: