Kinematic simulation of underwater crawling of dredging robot based on recurdyn
-
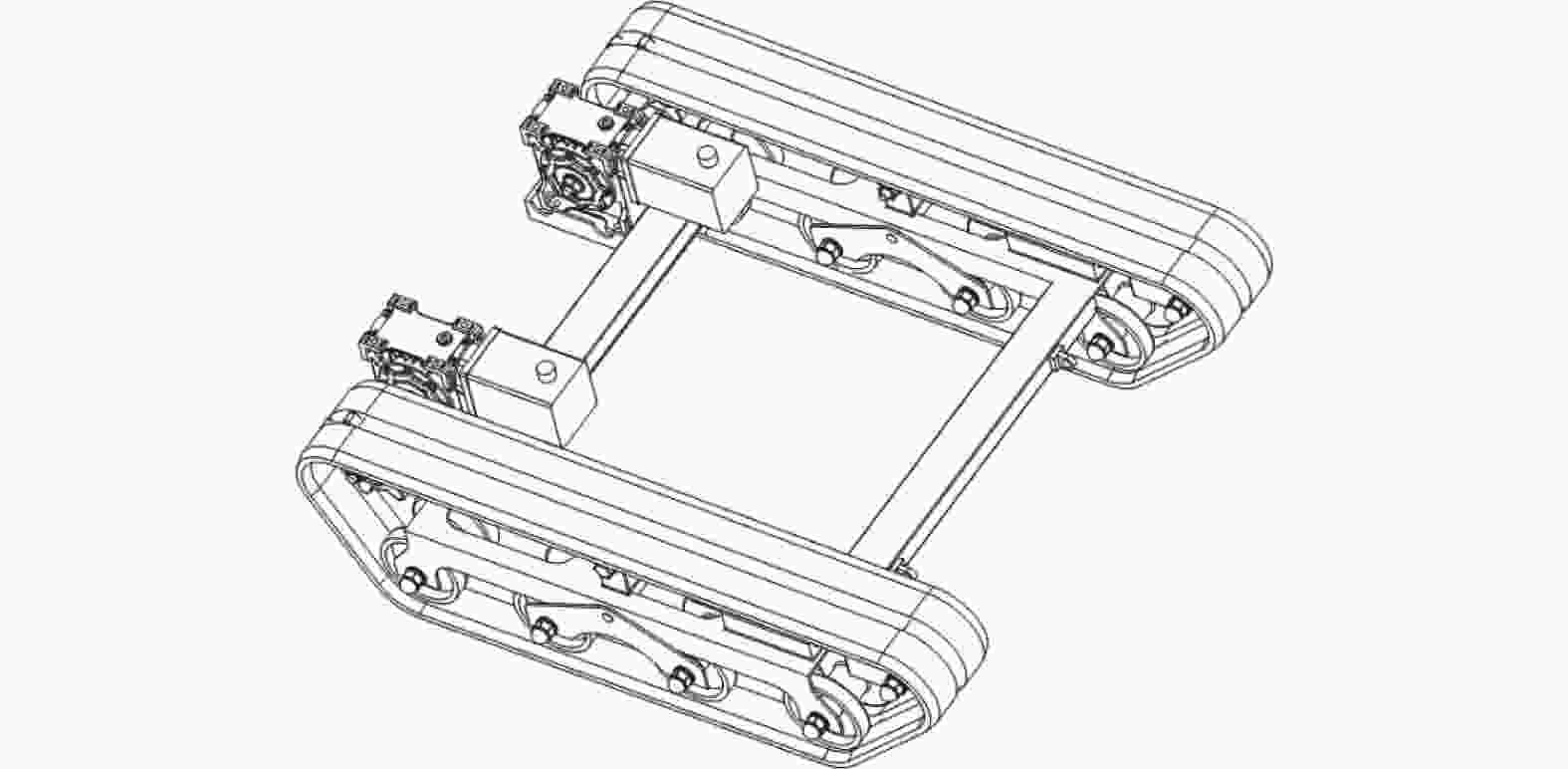
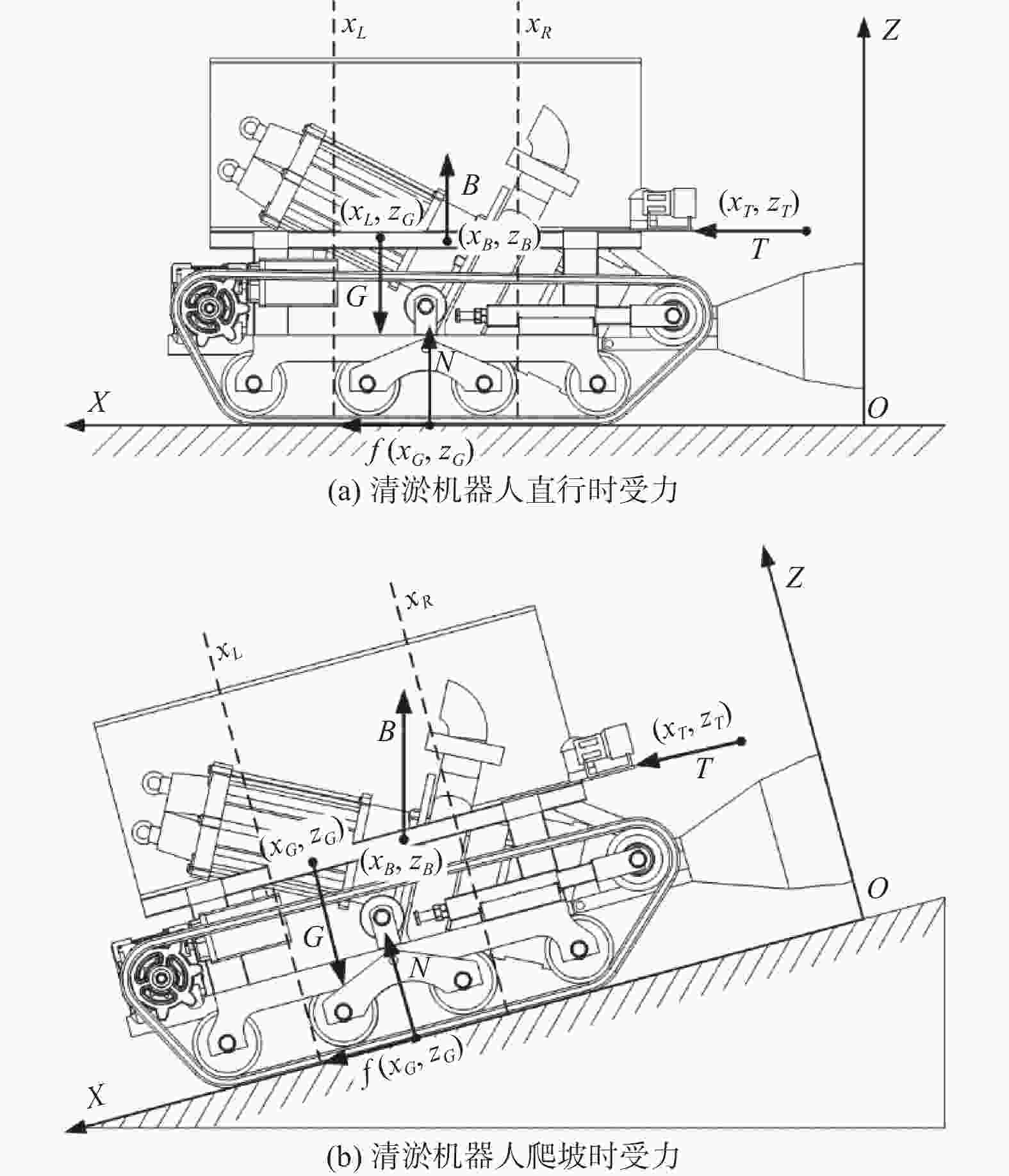
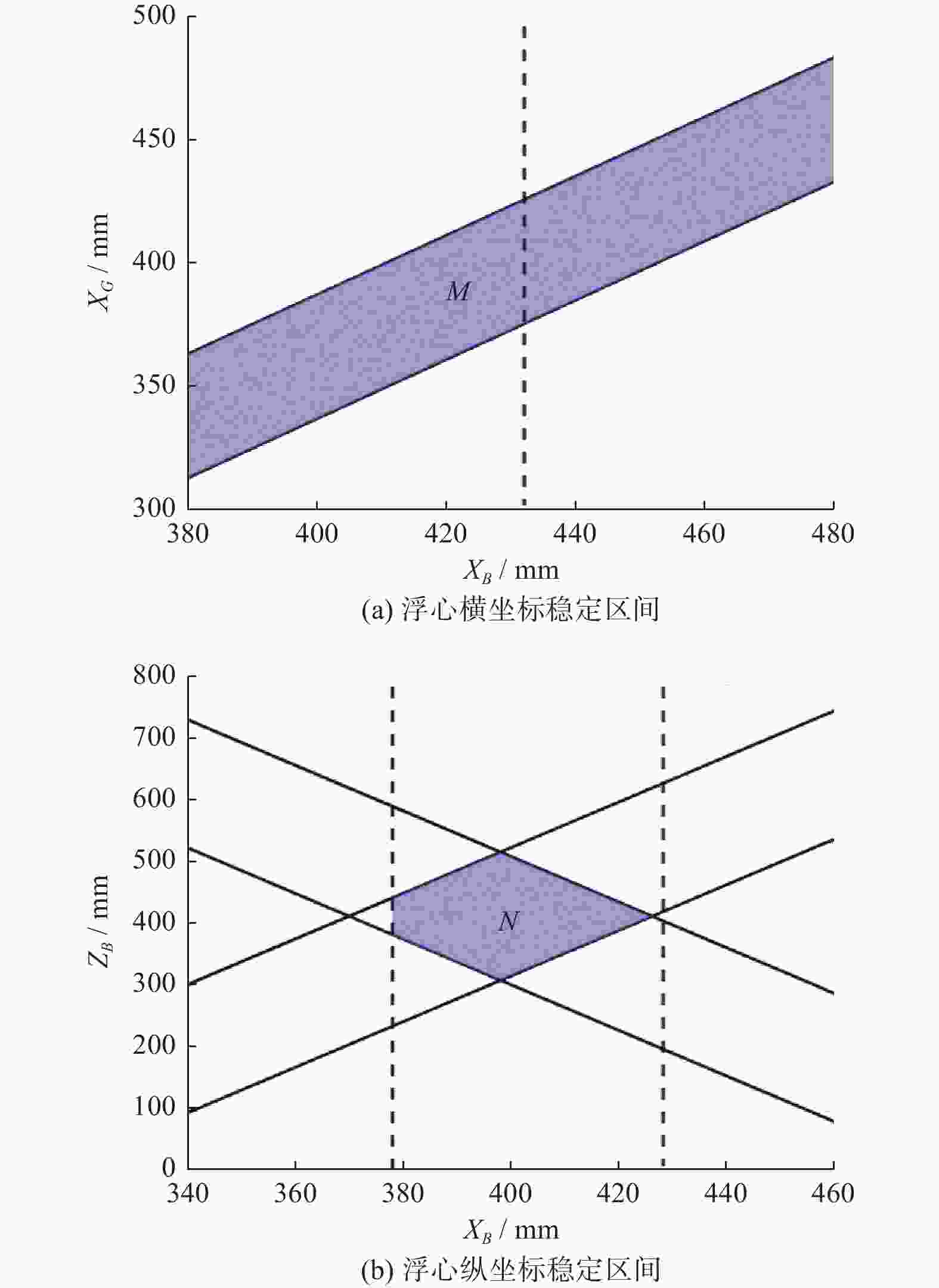
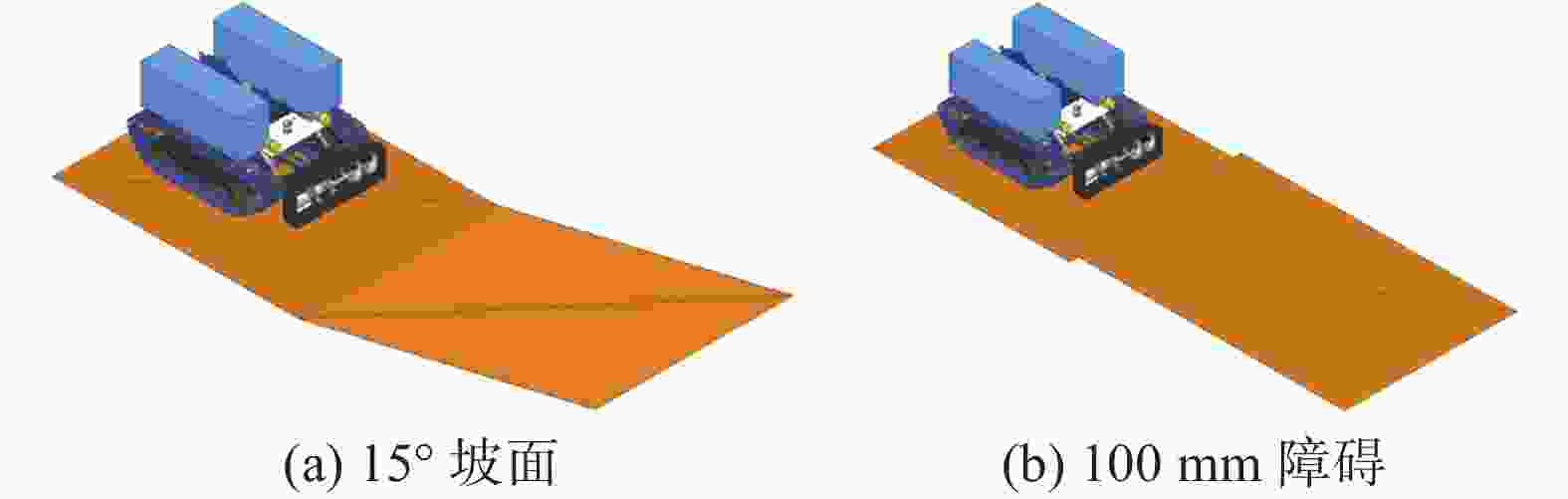
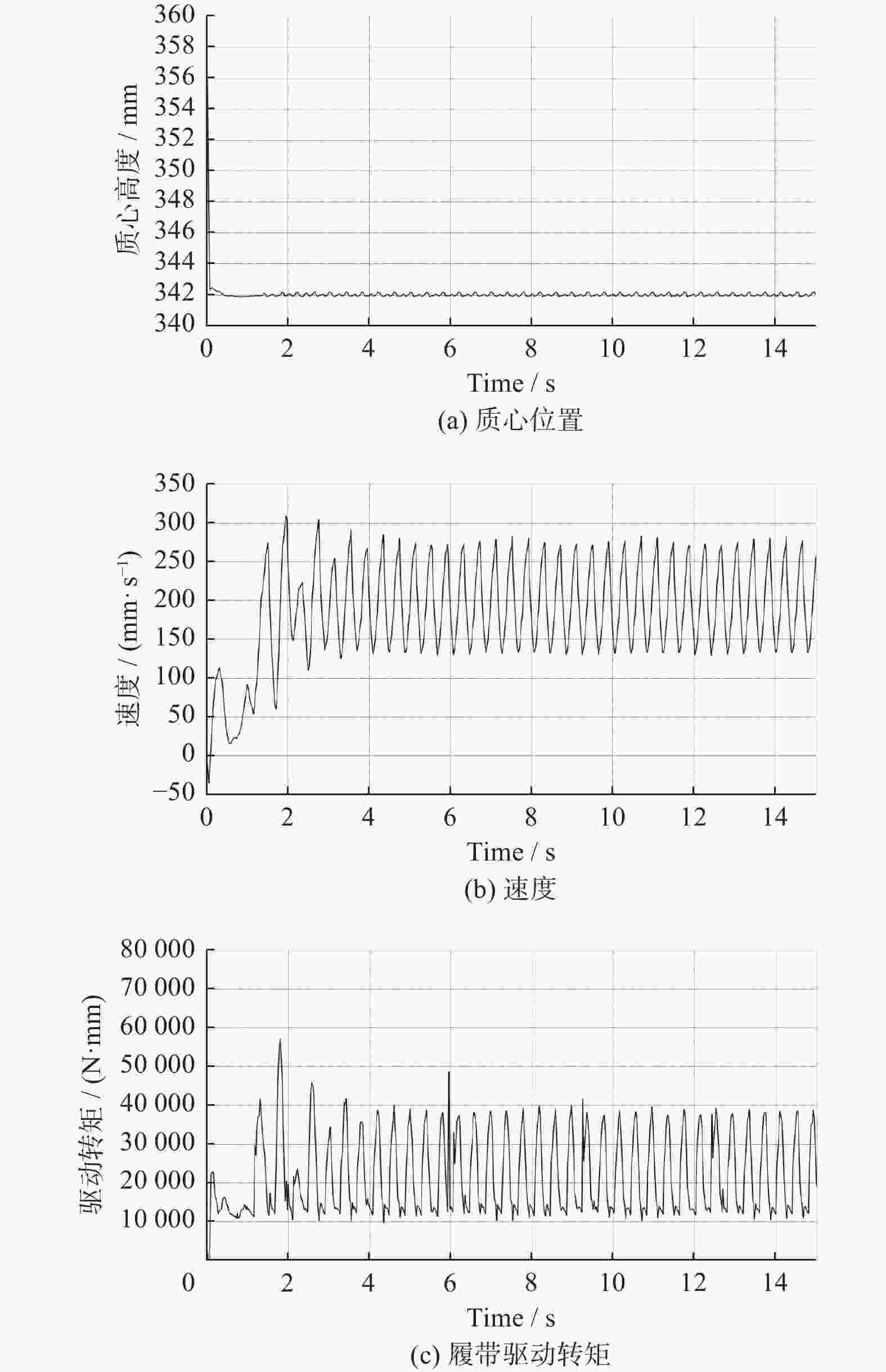
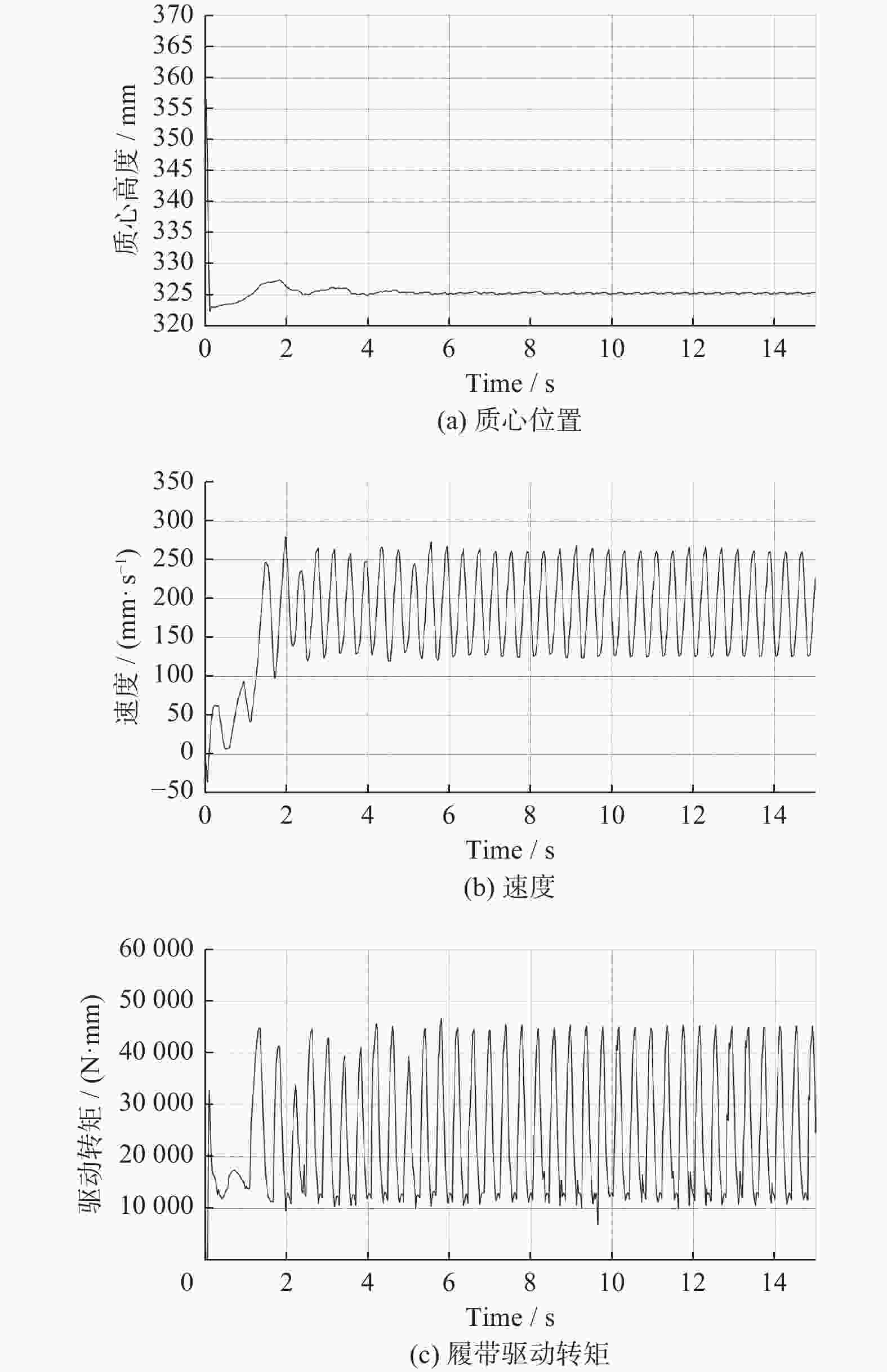
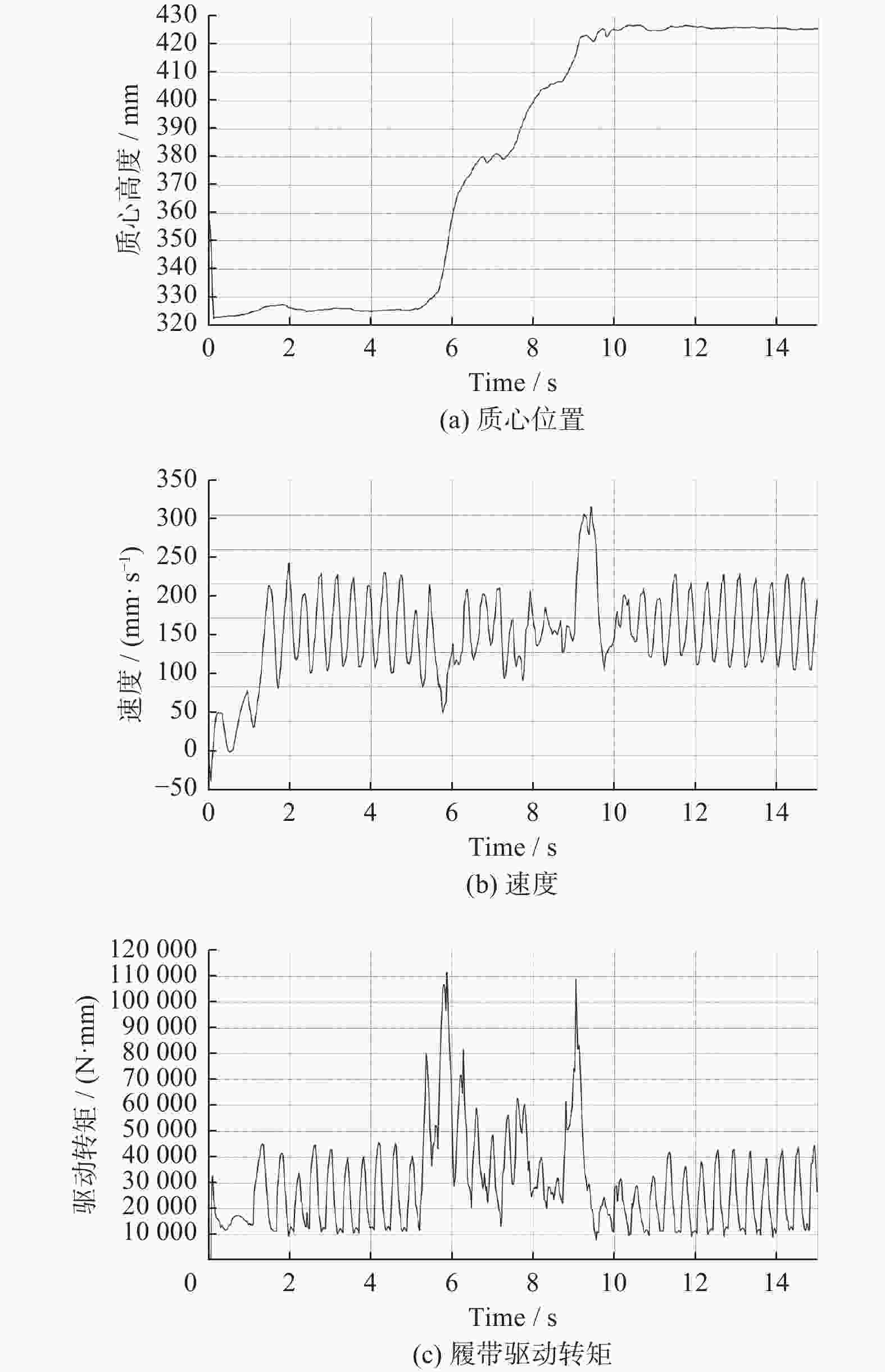
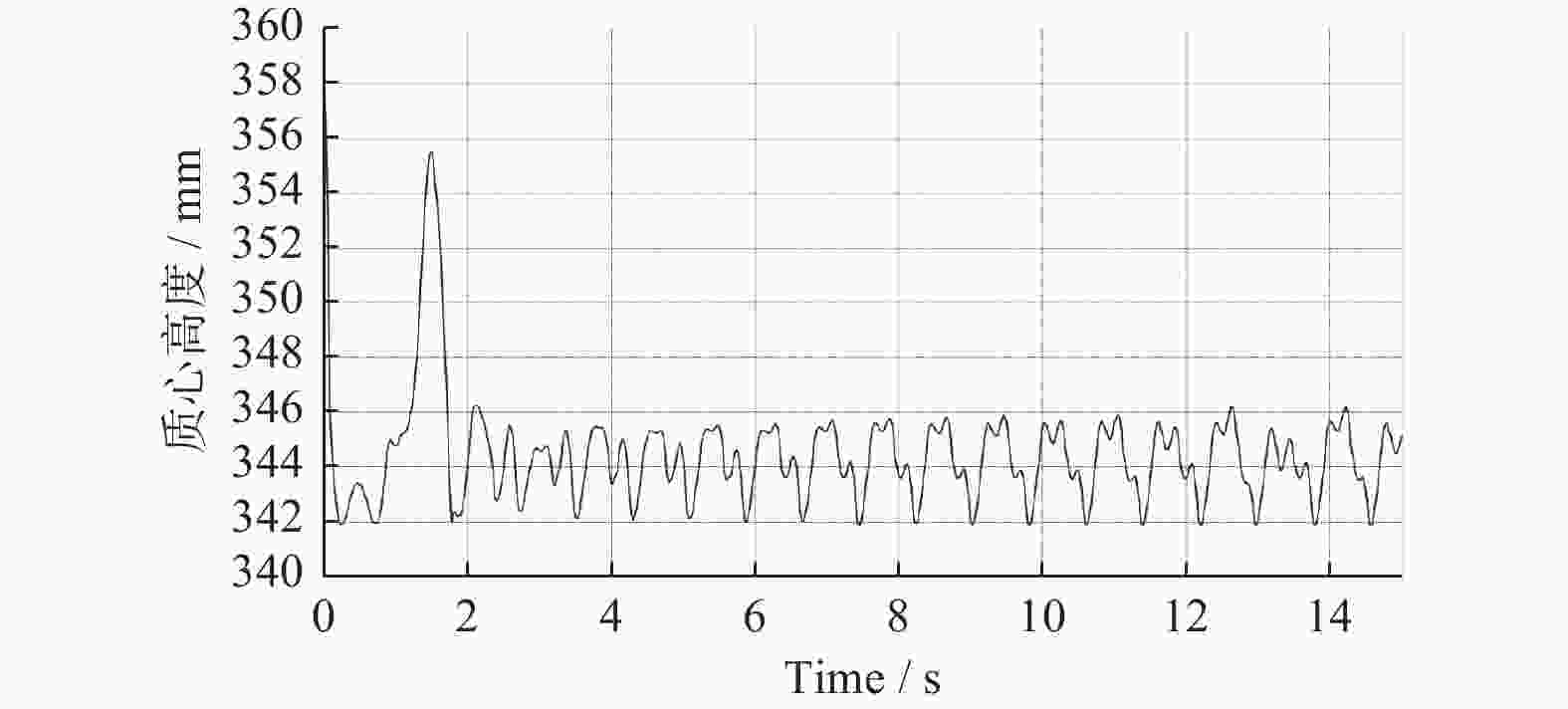
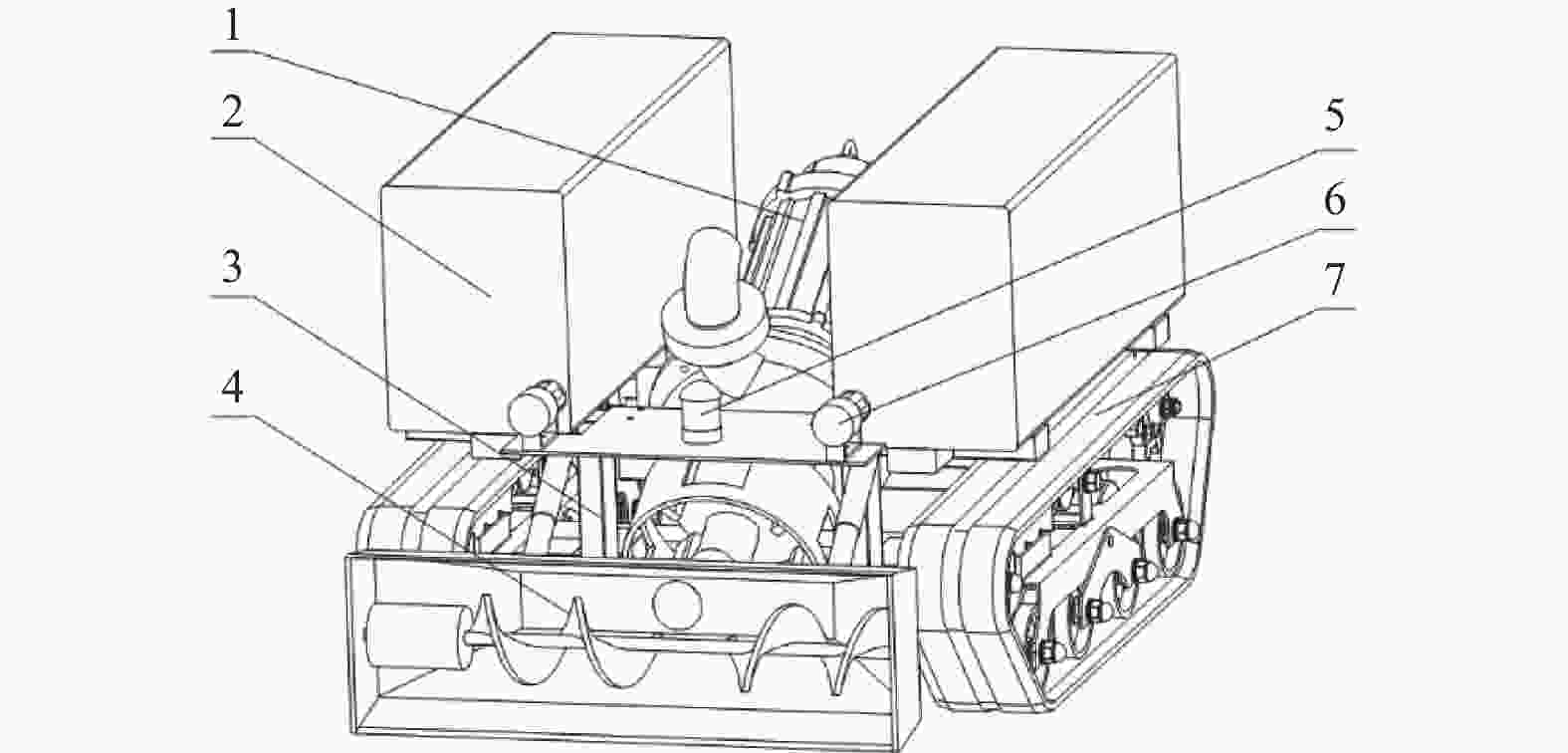
摘要: 针对沉淀池内工业淤泥难以清理的问题,设计一款能够适应复杂环境的履带式水下清淤机器人。机器人采用履带式移动机构,以适应松软泥层。对清淤机器人平地行驶、上下斜坡的稳定性进行分析,得到其稳定运行的浮心可行域。基于RecurDyn仿真软件搭建动力学模型,分析机器人在水底运行时不同类型的地形环境及工况。结果表明,浮心设置在浮心域内机器人的稳定性更高;清淤机器人的质心高度能够始终保持稳定,满足设计要求;清淤机器人能够稳定通过15°坡面和100 mm障碍,证明清淤机器人的设计能够适应水下复杂环境。
-
关键词:
- 履带式 /
- 清淤机器人 /
- 运动学 /
- RecurDyn仿真软件
Abstract: Aiming at the problem that industrial silt in settling tank was difficult to clean up, a crawler-type underwater dredging robot which can adapt to complex environment was designed. A crawler-type moving mechanism was used by the silt removal robot to adapt to soft mud layer. The stability of the dredging robot driving on flat ground and up and down slopes were analyzed, and the feasible region of the center of buoyancy of dredging robot running stably was obtained. The dynamic model of a dredging robot was built based on RecurDyn simulation software, and different types of terrain environment and working conditions were analyzed when the robot operating underwater. The results indicate that the buoyancy set in the center of buoyancy domain when the stability of the robot is higher. The height of the center of mass of the dredging robot can always remain stable and meet the design requirements. It is confirmed that the dredging robot can stably pass through 15° slopes and 100 mm obstacle, which proves that the design of the dredging robot can adapt to the complex underwater environment.-
Key words:
- tracked /
- dredging robot /
- kinematic /
- RecurDyn simulation software
-
表 1 机器人的设计指标
Table 1. Design index of dredging robot
参数名称 数值 整机尺寸/
(mm×mm×mm)长×宽×高:
1590×1010×875质量/kg 398.5 浮力/N 2984 重心坐标 (434,342) 表 2 软质地路面参数
Table 2. Soft pavement parameters
参数 取值 土壤变形模量kc 0.417 内摩擦的土壤变形模量kr 2.1888 × 10−2 土壤变形指数n 0.5 内聚力c 4.14 × 10−3 剪切阻力角度 13 剪切变形模数k 25 下沉比率 5 × 10−2 -
[1] 韩世旺, 王鲁元, 张兴宇, 等. 钢渣与污泥协同资源化研究进展[J] . 化学通报,2023,86(1):83 − 90,104. [2] VALPOLINI P. Infantry fighting vehicles and armoured personnel carriers[J] . Armada International,2013,67(6):236 − 246. [3] 张响亮, 张华, 熊根, 等. 基于RecurDyn的履带式消防机器人设计与爬梯运动学仿真[J] . 机械传动,2020,44(6):89 − 95. [4] 刘妤, 谢铌, 张拓, 等. 履带车辆软坡地面力学建模及行驶性能分析[J] . 机械设计,2021,38(3):110 − 118. [5] 王锦红, 林勇, 李海林. 基于Recurdy履带式海底行走机构不同工况性能分析[J] . 机械传动,2017,41(5):45 − 52. [6] 李硕, 吴园涛, 李琛, 等. 水下机器人应用及展望[J] . 中国科学院院刊,2022,37(7):910 − 920. [7] PURSER A, THOMSEN L, BARNES C, et al. Temporal and spatial benthic data collection via an Internet operated deep sea crawler[J] . Methods in Oceanography,2013,5:1 − 18. doi: 10.1016/j.mio.2013.07.001 [8] 翟旭强, 张俊俊, 王皓冉, 等. 水下浮游爬行式机器人结构设计与研究[J] . 制造业自动化,2021,43(5):41 − 45, 55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0134.2021.05.010 [9] 肖顺. 履带式变体移动机器人样机设计与关键技术研究[D]. 北京: 北方工业大学, 2023. [10] 王南丁. 消防机器人履带行走装置设计及运动学仿真研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2015. [11] 翟旭强. 消力池水下巡检机器人结构设计与研究[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2020. [12] INOUE T, SHIOSAWA T, TAKAGI K. Dynamic analysis of motion of crawler-type remotely operated vehicles[J] . IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering,2013,38(2):375 − 382. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2012.2225292 [13] 郭进宝, 周悦, 郭威, 等. 海岸带履带机器人底盘参数优化与行驶仿真分析[J] . 制造业自动化,2022,44(12):85 − 90. [14] 陈安成, 穆希辉, 杜峰坡, 等. 基于RecurDyn的小型履带车的建模与仿真[J] . 机械设计,2013,30(10):36 − 39. -





 下载:
下载: