Research on person re-identification by fusing posture information and attention mechanisms
-
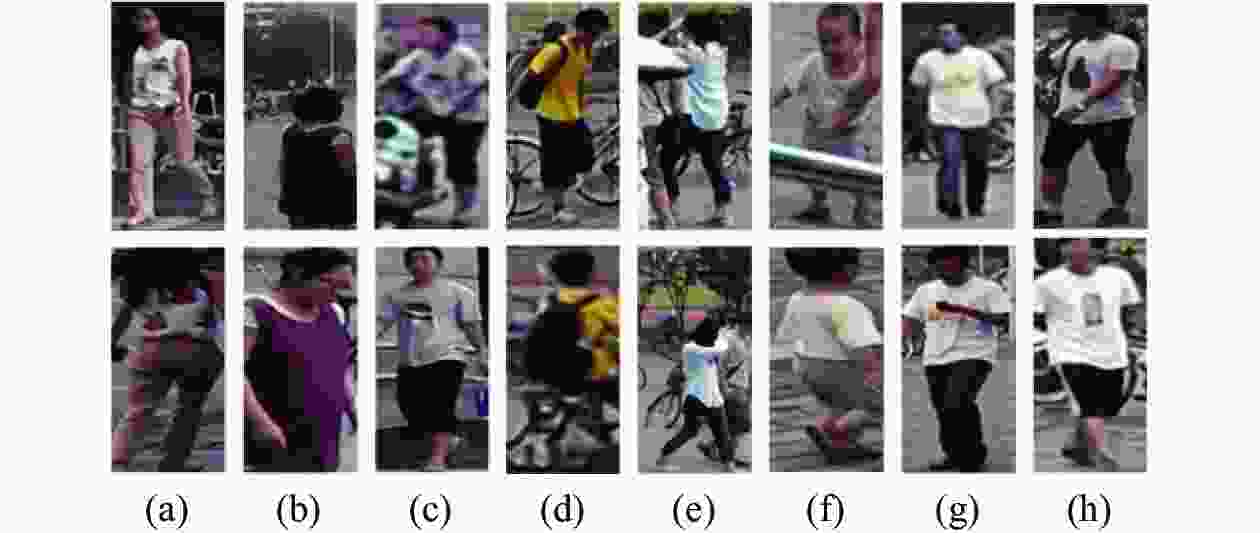
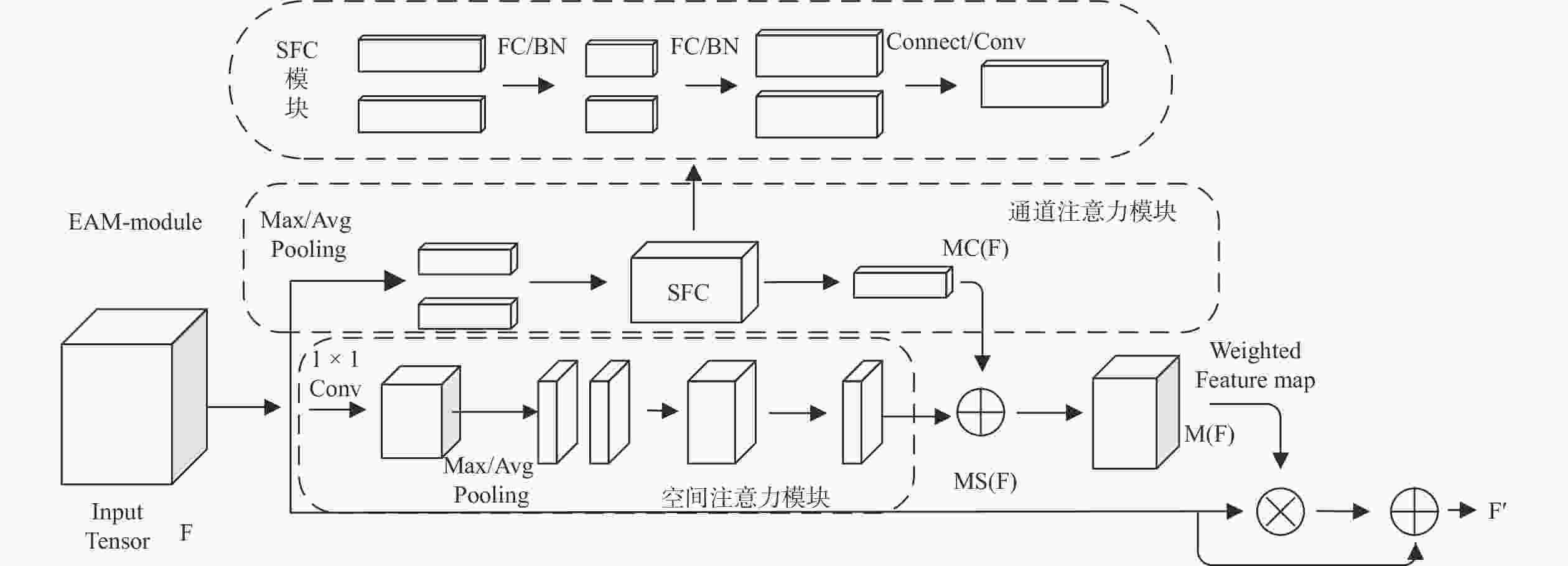
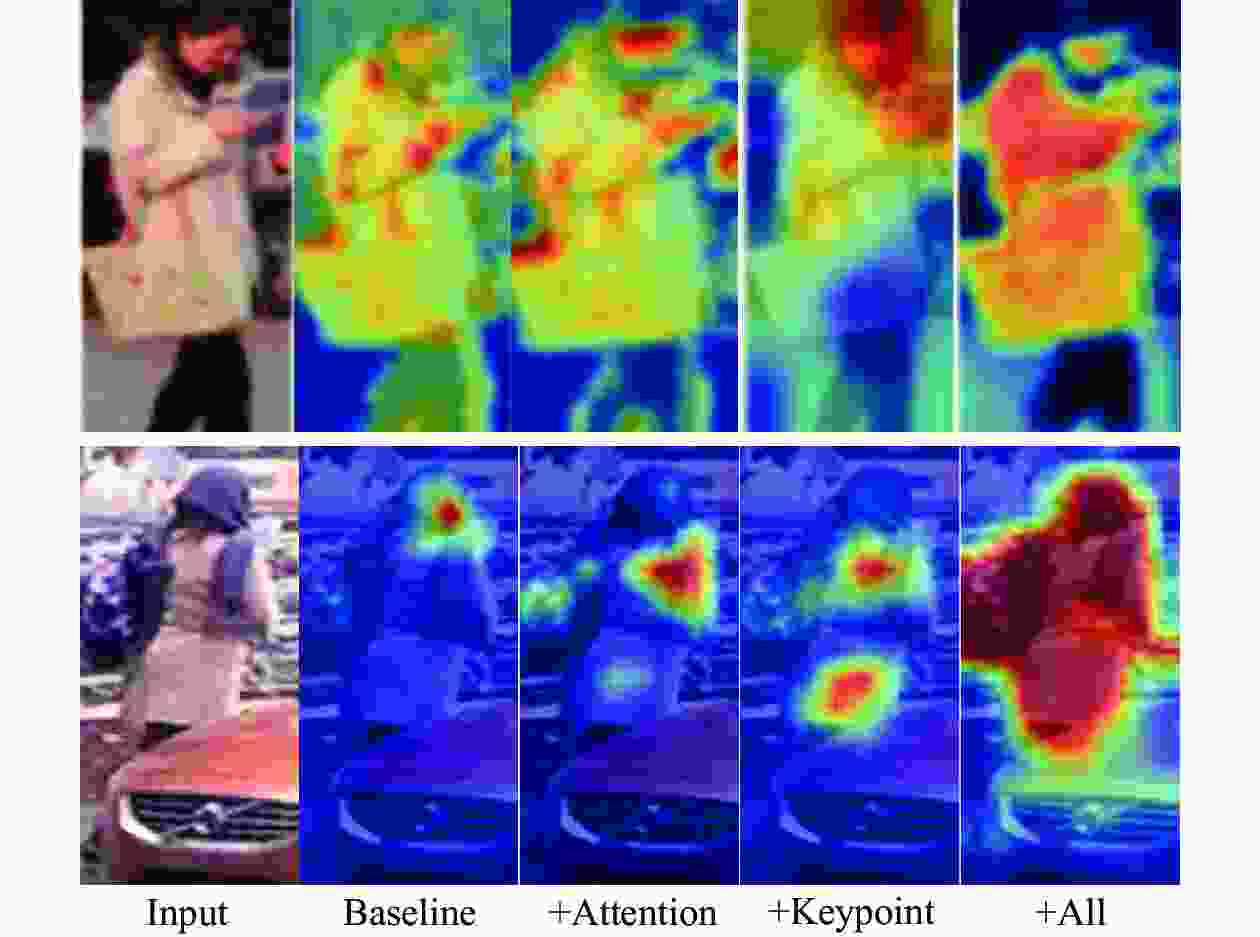
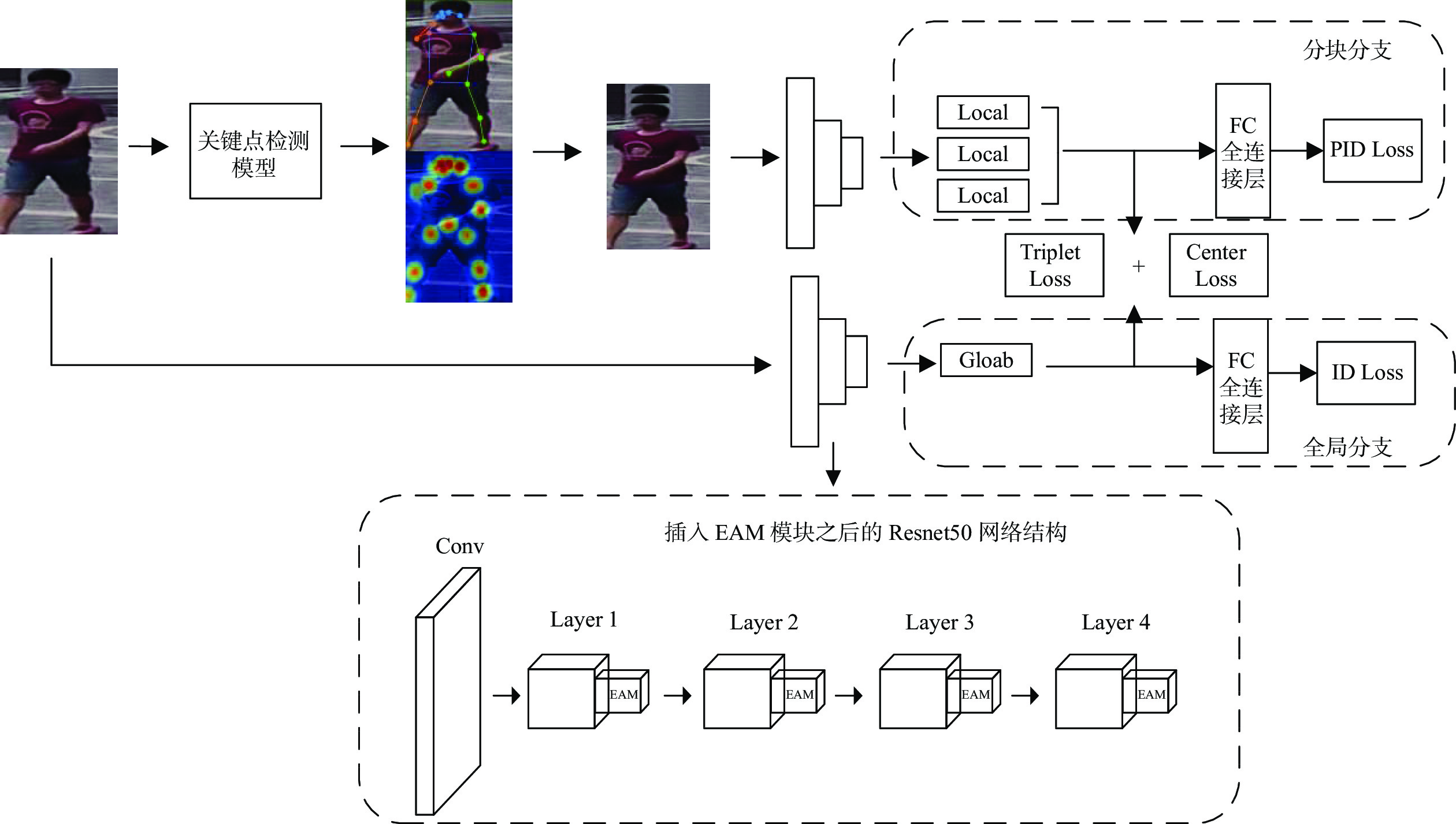
摘要: 针对行人重识别(person re-identification, Re-ID)任务中行人遮挡以及背景信息杂乱不便于提取具有辨识度特征的问题,引入人体关键点模型定位出行人的关键点坐标以便于消除背景信息,根据关键点坐标将图片分割成具有语义信息的区域块。对于骨干网络,为使其提取的特征更加鲁棒,设计一个强化注意力模块(enhanced attention module, EAM),使网络自动分配权重,最终得到更加具有辨识度的特征向量。最后将这些区域块和整体图片送入修改后的注意力机制的神经网络并且联合多个损失一起优化网络。在几个行人重识别数据集试验验证了本研究提出方法优于大多数方法。试验结果还表明该网络针对跨域以及遮挡问题也起到积极作用。Abstract: To address the problem of pedestrian occlusion and messy background information in the task of pedestrian re-identification (Re-ID), the human body key point model was adopted to locate the key point information of the pedestrians to eliminate the background information, and the image was segmented into semantic information based on the key point information. In order to make the extracted features of backbone network more robust, enhanced attention module (EAM) was designed, which allows the network to automatically assign weights, and the more recognizable feature vectors were finally obtained. These parts and the overall image were fed into a neural network that incorporates the modified attention mechanism and optimized the network by combining multiple losses. Experiments on several pedestrian re-recognition datasets validate that the proposed method outperforms most state-of-the-art methods. In addition, the experimental results also show that the network has a positive effect on the cross-domain and occlusion problems.
-
表 1 在Market1501以及MSMT17上的试验结果
Table 1. Test results on Market1501 dataset
Method Market1501 MSMT17 Rank1 mAP Rank1 mAP OSNet[13] 94.8 84.9 73.5 88.6 HOReID[14] 94.2 84.9 — — NFormer[15] 95.7 93.0 80.8 62.2 RGA-SC[16] 96.1 88.4 80.3 57.5 AlignedReID + + [17] 91.0 77.6 80.7 68.0 BSnet[18] 92.5 — 71.7 — CNet[19] 95.7 88.5 — — IANet[20] 94.4 83.1 75.5 46.8 Pose-guided[21] 93.5 78.6 — — base 94.0 83.4 75.7 51.5 ours 95.4 86.5 82.3 68.6 表 2 在遮挡数据集P-DukeMTMC上的试验结果
Table 2. Test results on P-DukeMTMC of occluded dataset
表 3 在Market1501数据集上的试验结果
Table 3. Test results on Market1501 dataset
Resnet50 Keypoint Attention Rank1 mAP √ 94.0 83.4 √ √ 95.0 85.3 √ √ 94.5 84.9 √ √ √ 95.4 86.5 表 4 在P-DukeMTMC遮挡数据集上的结果
Table 4. Test results on P-DukeMTMC of occluded dataset
Resnet50 Keypoint Attention Rank1 mAP √ 55.5 46.2 √ √ 58.6 49.3 √ √ 57.1 47.6 √ √ √ 59.4 50.9 表 5 针对跨域数据集上进行试验
Table 5. Experimental results on cross-domain datasets
Mode Ma→MN MN→Ma Rank1 mAP Rank1 mAP Base 33.2 18.5 41.3 20.5 + attention 36.4 20.3 45.6 23.1 + openpose 38.5 22.7 47.1 25.5 our 39.4 23.6 48.5 27.4 -
[1] 罗浩, 姜伟, 范星, 等. 基于深度学习的行人重识别研究进展[J] . 自动化学报,2019,45(11):2032 − 49. [2] 马丁. 面向复杂场景的行人重识别关键技术研究 [D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2022. [3] 沈欣怡. 基于深度学习行人重识别研究 [D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2022. [4] ZHENG L, HUANG Y J, LU H, et al. Pose invariant embedding for deep person re-identification[J] . IEEE Trans Image Process,2019,28(9):4500 − 4509. [5] ZHAO H Y, TIAN M Q, SUN S Y, et al. Spindle net: Person re-identification with human body region guided feature decomposition and fusion[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017. [6] SU C, LI J, ZHANG S, et al. Pose-driven deep convolutional model for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Sydney: IEEE, 2013. [7] SUH Y, WANG J, TANG S, et al. Part-aligned bilinear representations for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Munich: Springer, 2018. [8] HU J, SHEN L, ALBANIE S, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J] . IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2020,42(8):2011 − 23. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372 [9] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J-Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Munich: Springer, 2018. [10] PARK J, WOO S, LEE J Y, et al. BAM: Bottleneck attention module[EB/OL]. (2018-07-17)[2023-04-03]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1807.06514. [11] LI Y, YANG S, LIU P, et al. SimCC: A simple coordinate classification perspective for human pose estimation[C]//Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Tel Aviv: Springer, 2022. [12] CHEN K, WANG J, PANG J, et al. MMDetection: Open MMLab detection toolbox and benchmark[EB/OL]. (2019-06-17)[2022-12-21]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.07155. [13] ZHOU K, YANG Y, CAVALLARO A, et al. Omni-scale feature learning for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul: IEEE, 2019. [14] WANG G, YANG S, LIU H, et al. High-order information matters: Learning relation and topology for occluded person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle: IEEE, 2020. [15] WANG H, SHEN J, LIU Y, et al. NFormer: Robust person re-identification with neighbor transformer[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New Orleans: IEEE, 2022. [16] ZHANG Z, LAN C, ZENG W, et al. Relation-aware global attention for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans: IEEE, 2020. [17] LUO H, JIANG W, ZHANG X, et al. AlignedReID plus plus: Dynamically matching local information for person re-identification[J] . Pattern Recognition: The Journal of the Pattern Recognition Society,2019,94:53 − 61. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.05.028 [18] CHEN G, ZOU G, LIU Y, et al. Few-shot person re-identification based on feature set augmentation and metric fusion[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 125: 106761. [19] ZHANG G, LIN W, CHANDRAN A K, et al. Complementary networks for person re-identification[J] . Information Sciences,2023,633:70 − 84. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2023.02.016 [20] HOU R, MA B, CHANG H, et al. Interaction-and-aggregation network for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach: IEEE, 2019. [21] KHATUN A, DENMAN S, SRIDHARAN S, et al. Pose-driven attention-guided image generation for person re-identification[EB/OL]. (2021-04-28)[2023-04-21]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2104.13773. [22] HE L, LIANG J, LI H, et al. Deep spatial feature reconstruction for partial person re-identification: Alignment-free approach[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake: IEEE, 2018. [23] GAO S, WANG J, LU H, et al. Pose-guided visible part matching for occluded person ReID[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Washington: IEEE, 2020. [24] SUN Y, ZHENG L, YANG Y, et al. Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline)[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Salt Lake: IEEE, 2018. [25] JIN H, LAI S, QIAN X J I T O C, et al. Occlusion-sensitive person re-identification via attribute-based shift attention[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 32(4): 2170−2185. -





 下载:
下载: