Attitude control of shockwave robot based on time-of-flight sensor
-
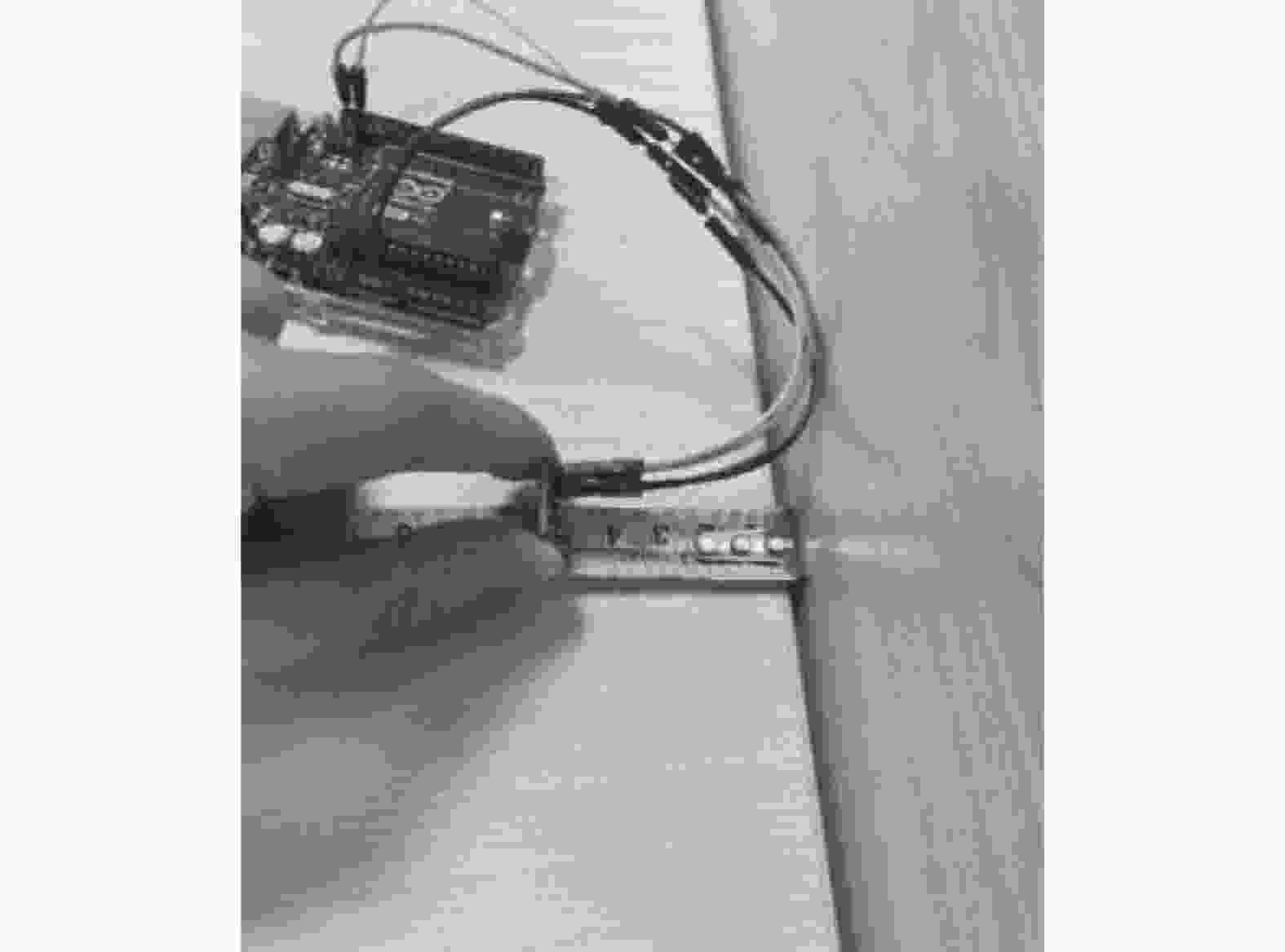
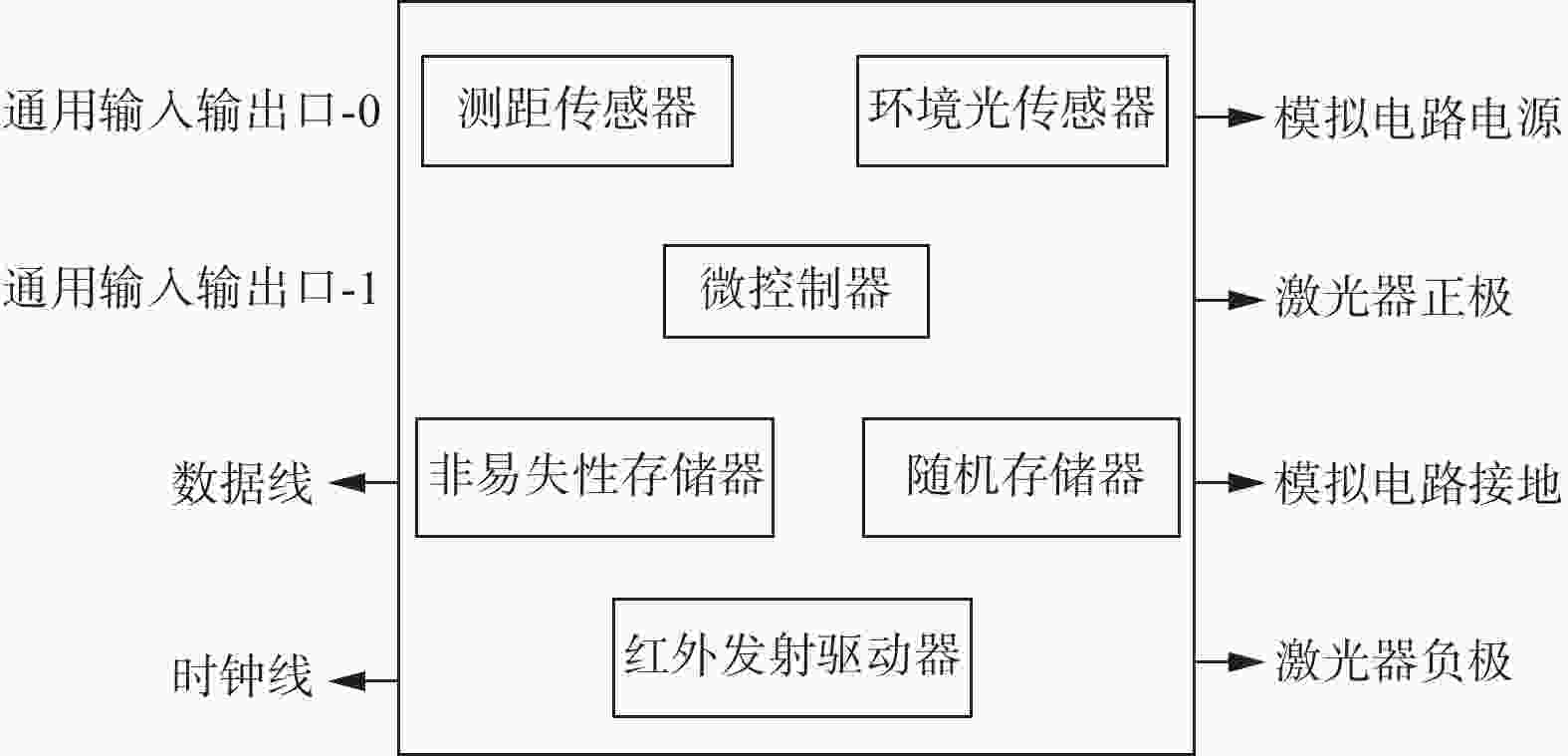
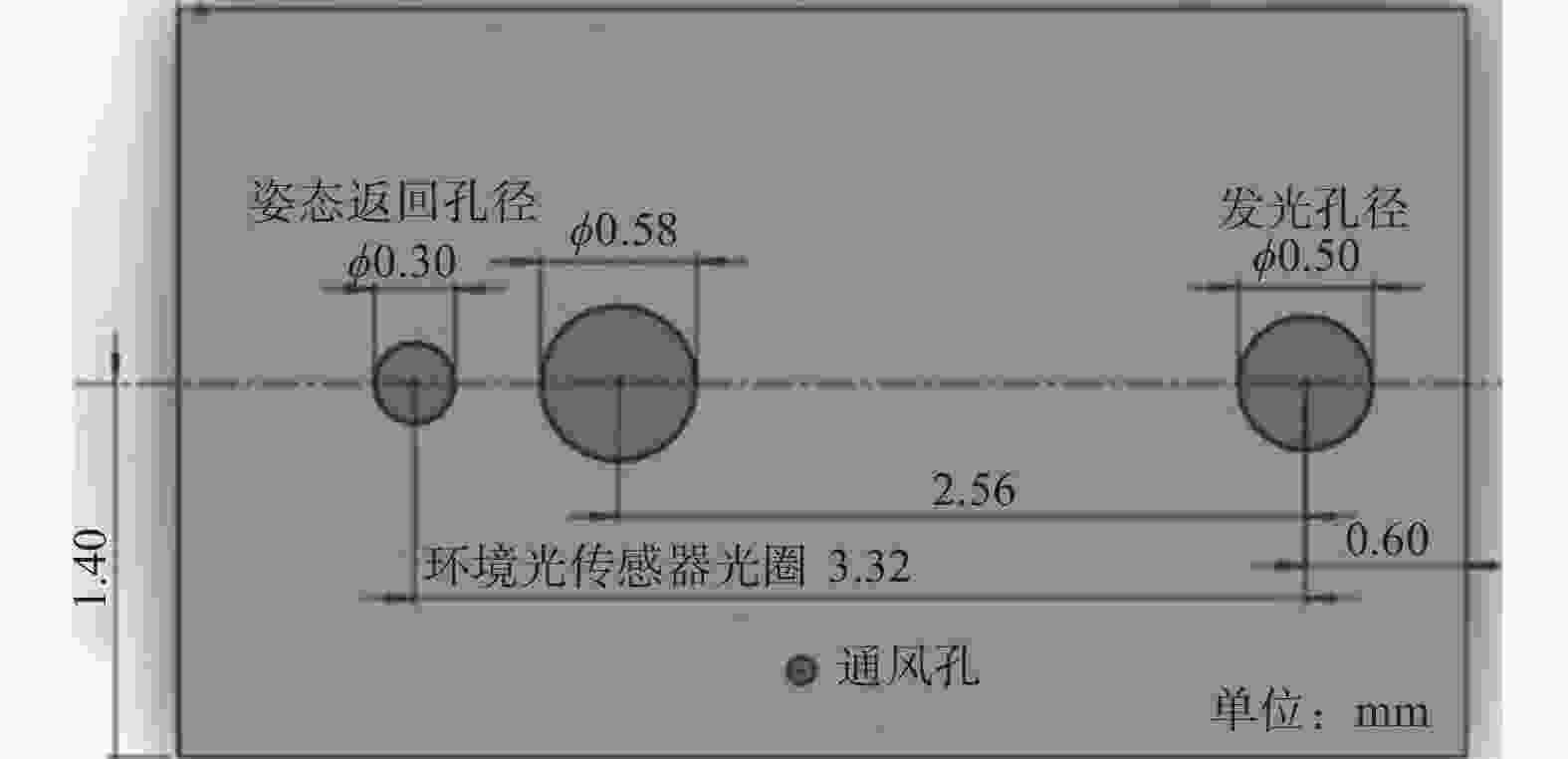
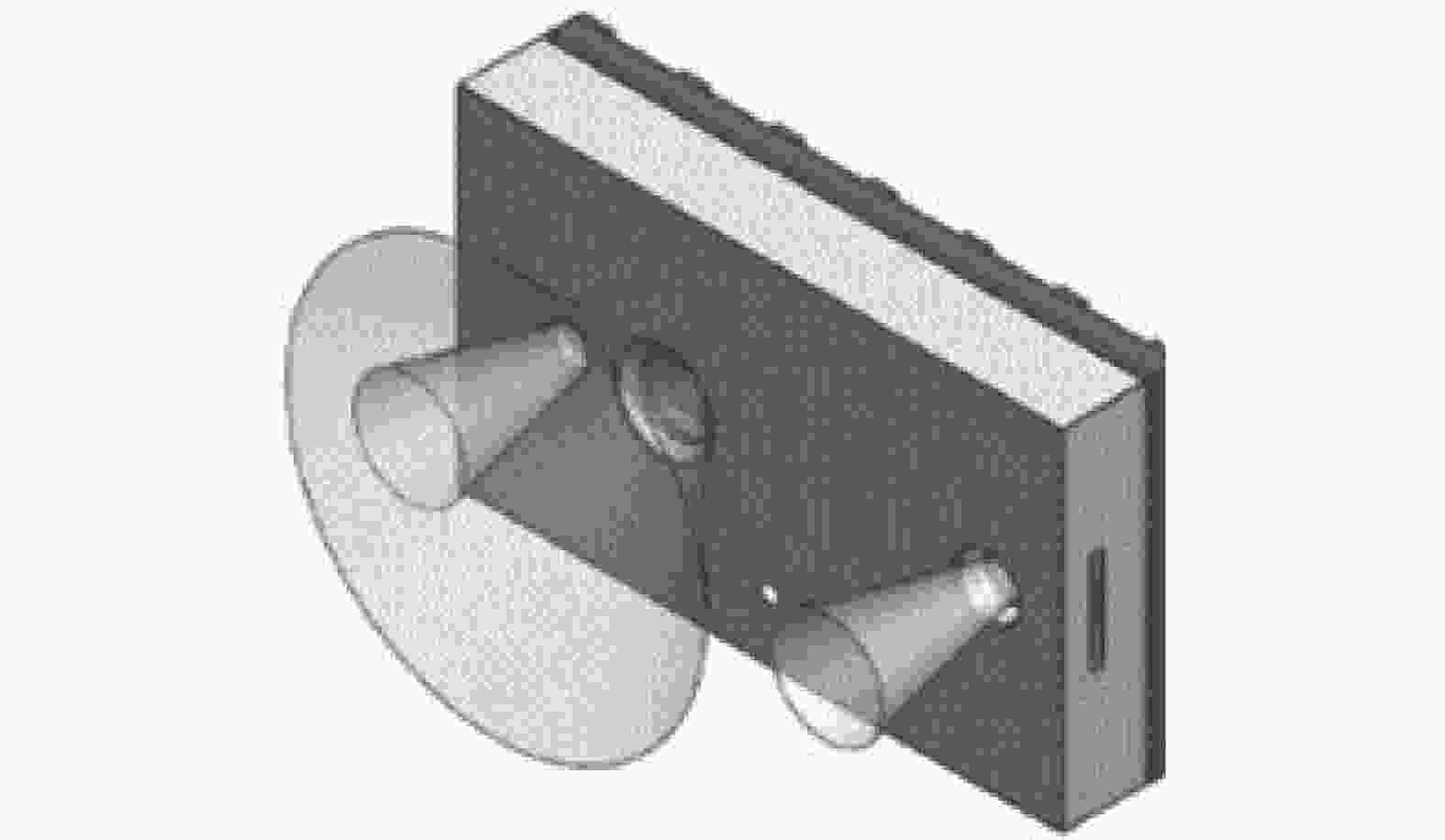
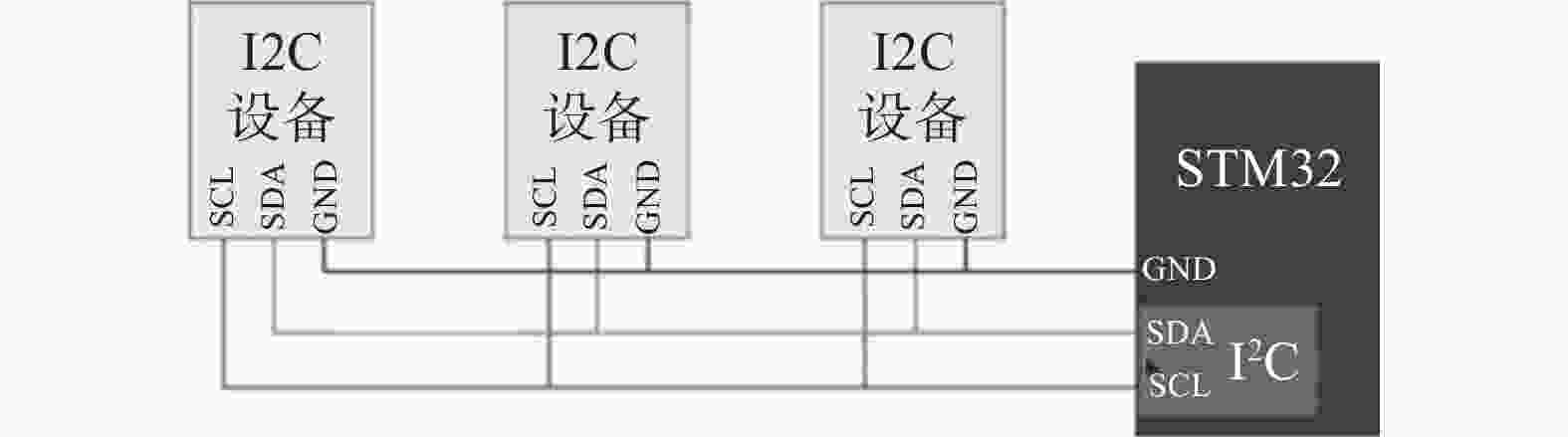
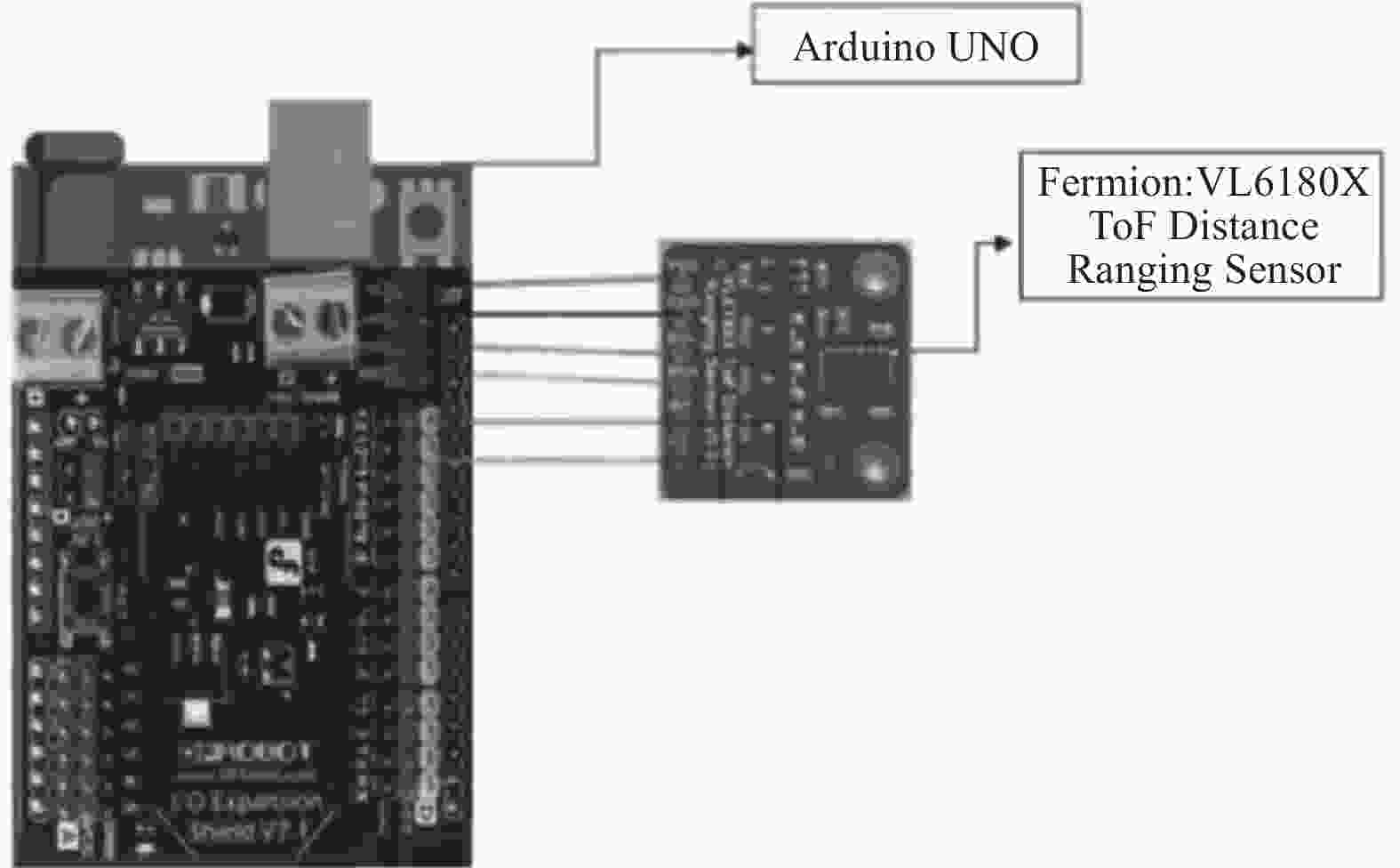
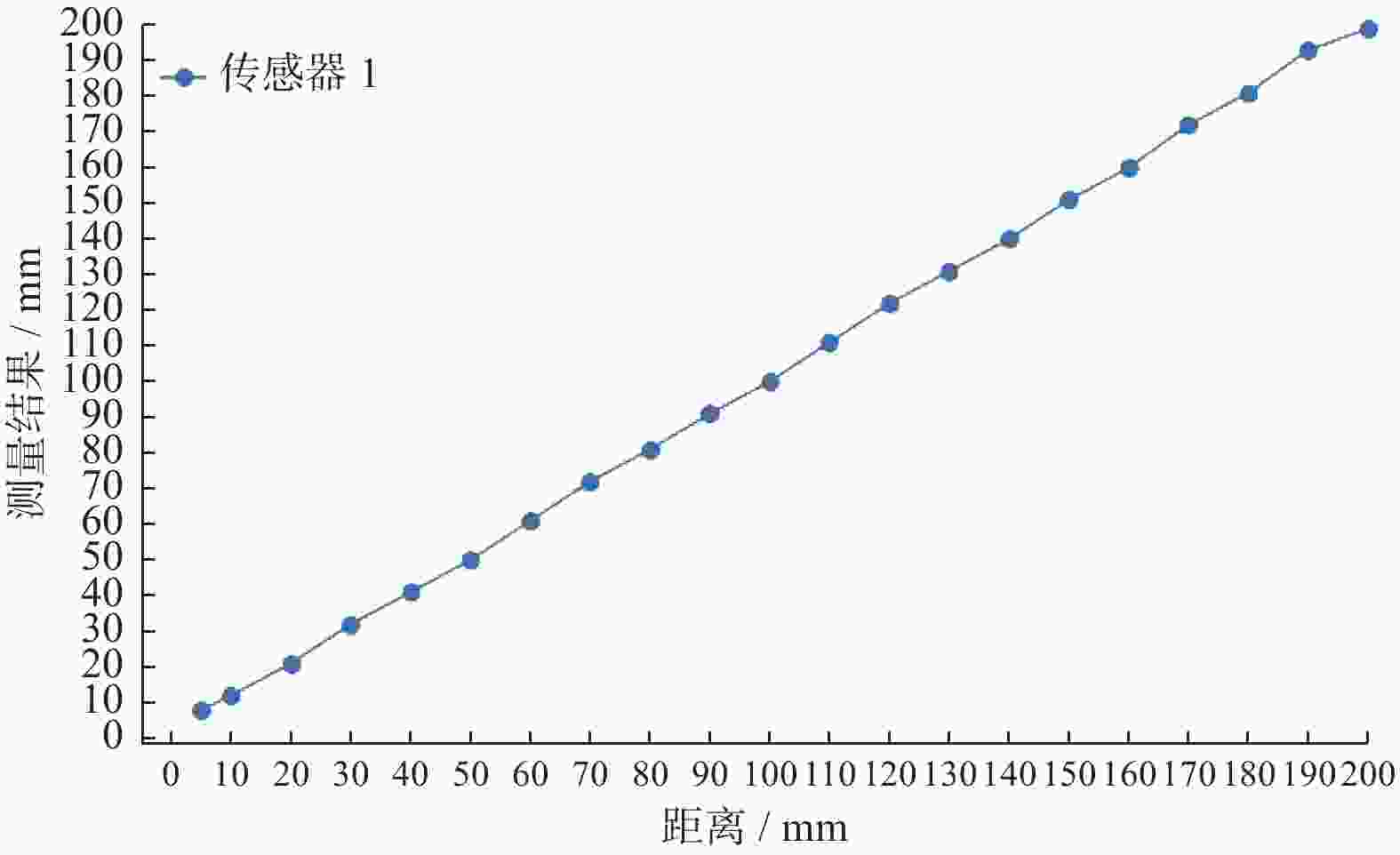
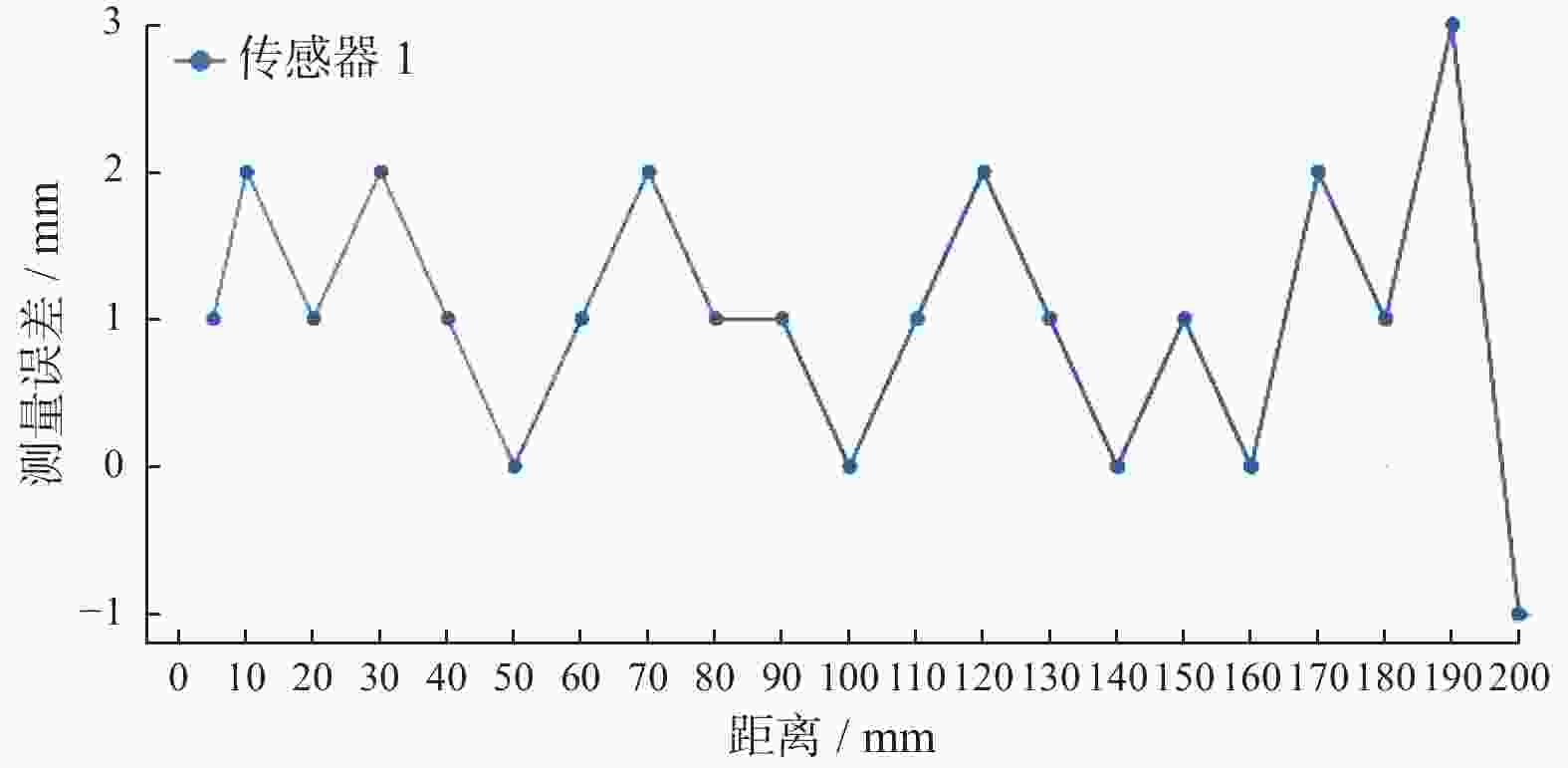
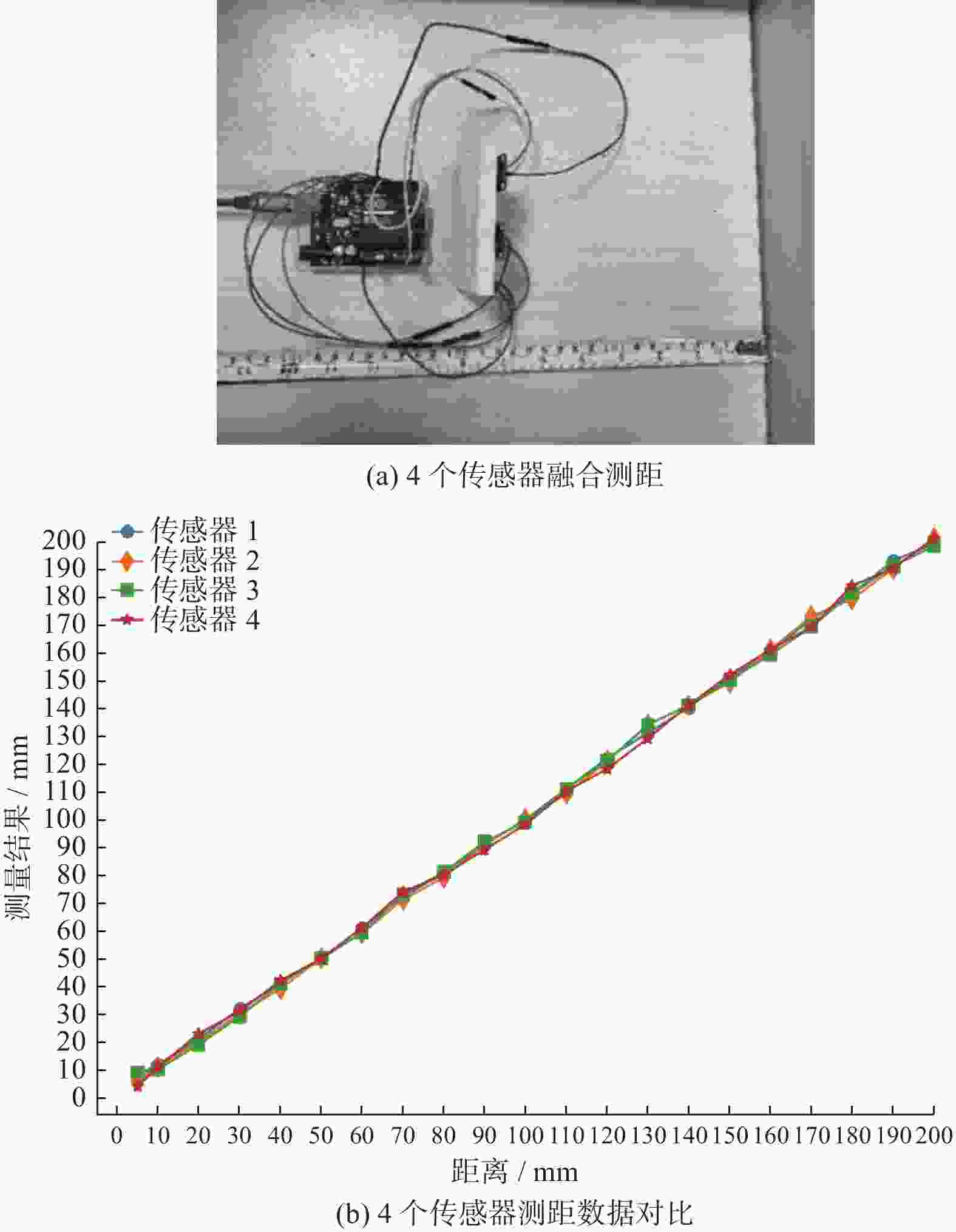
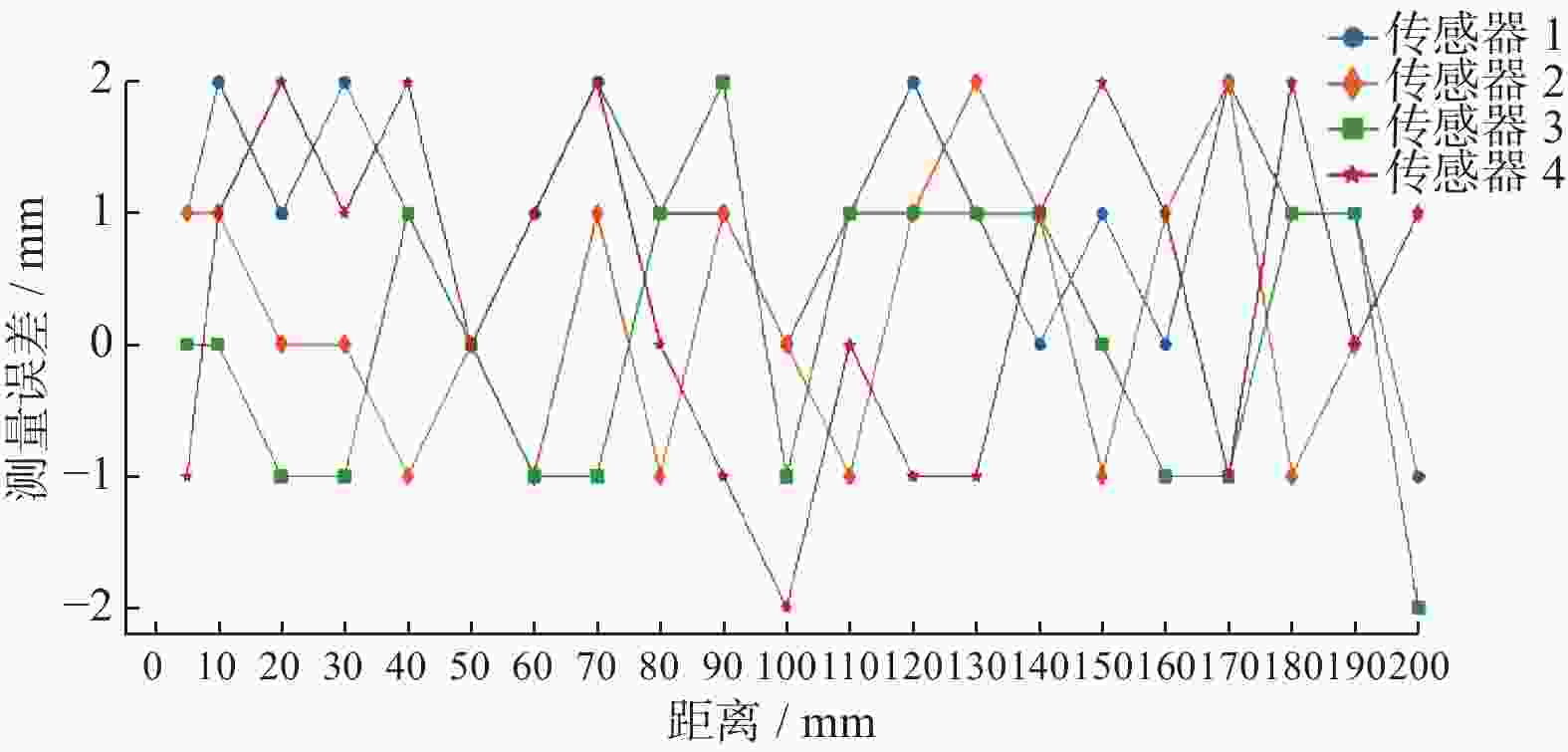
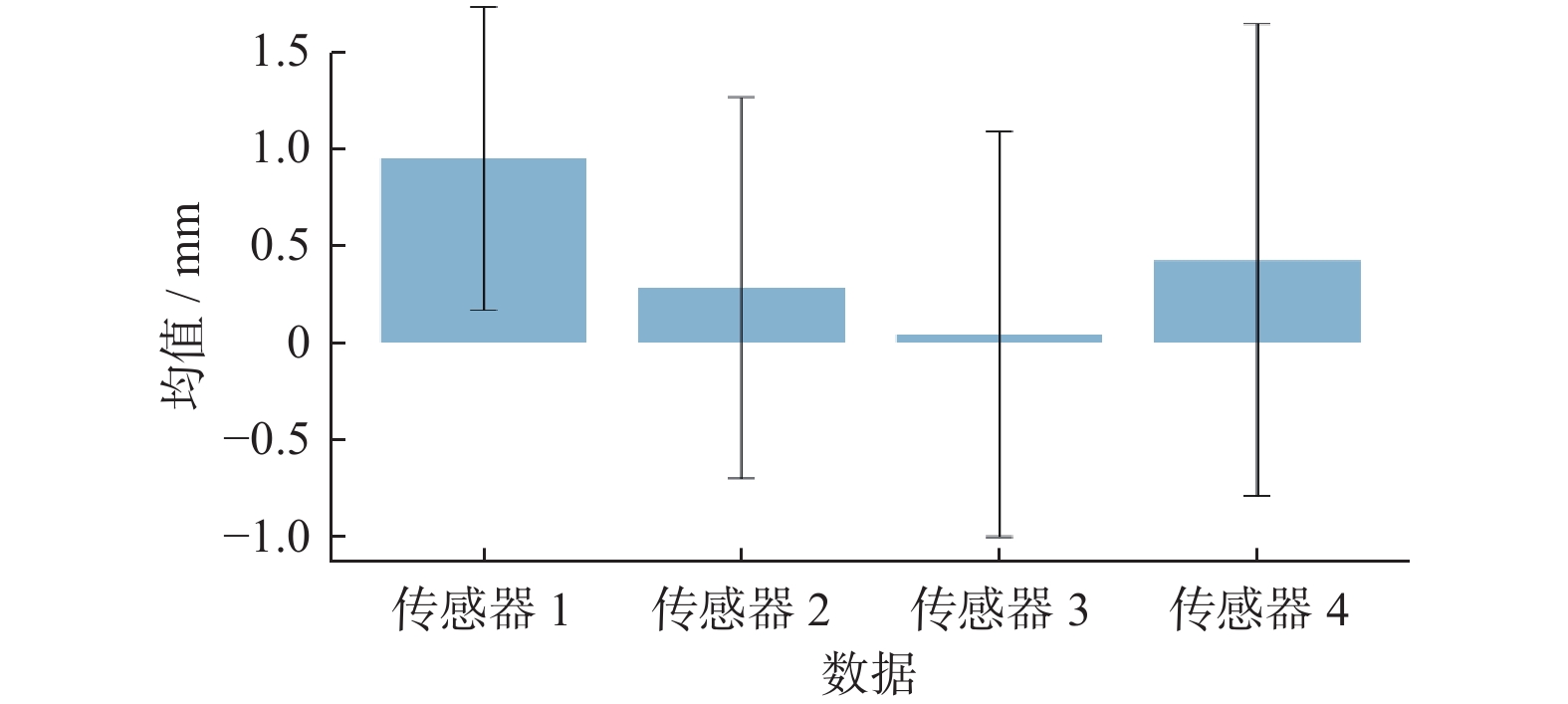
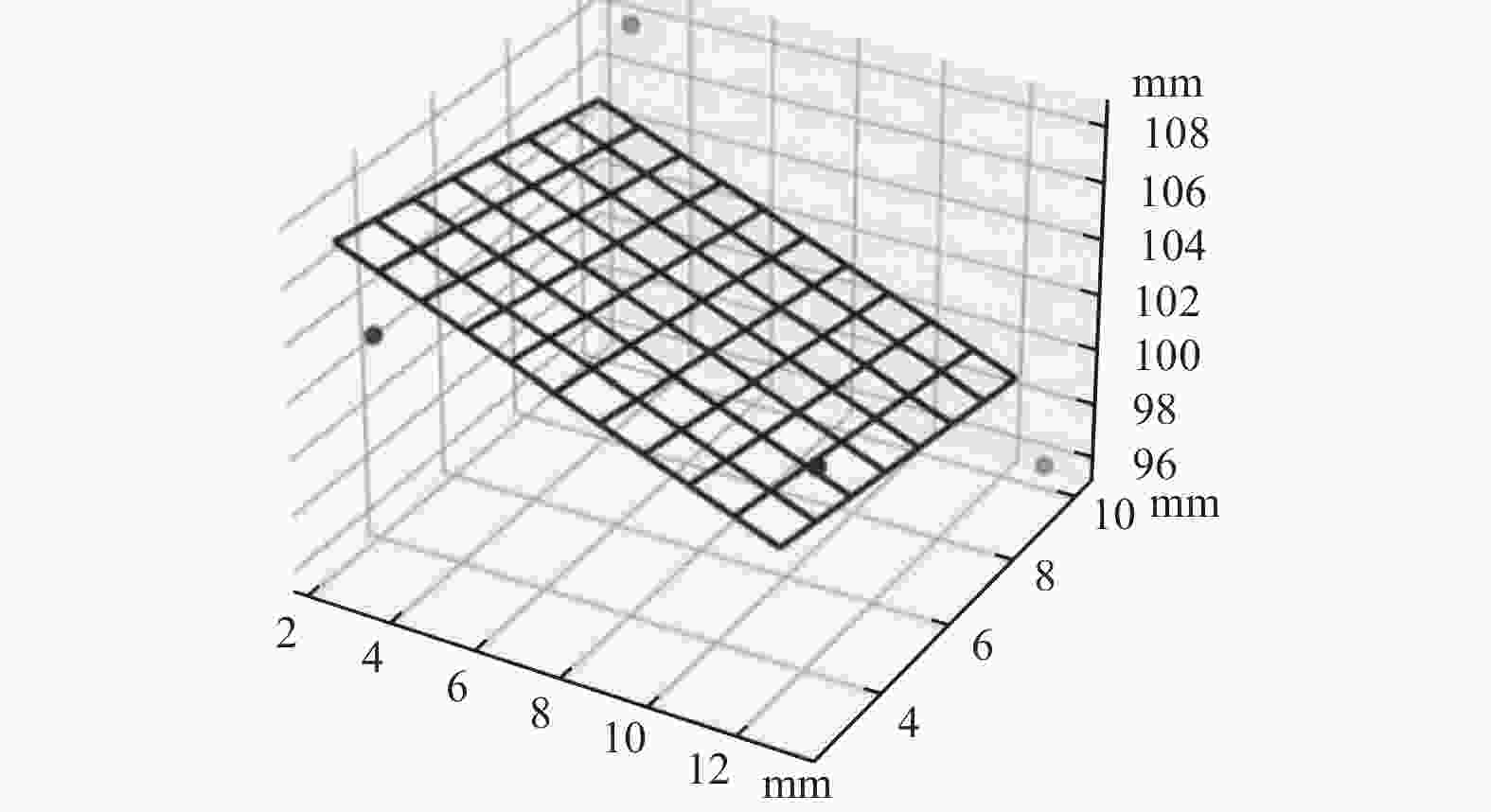
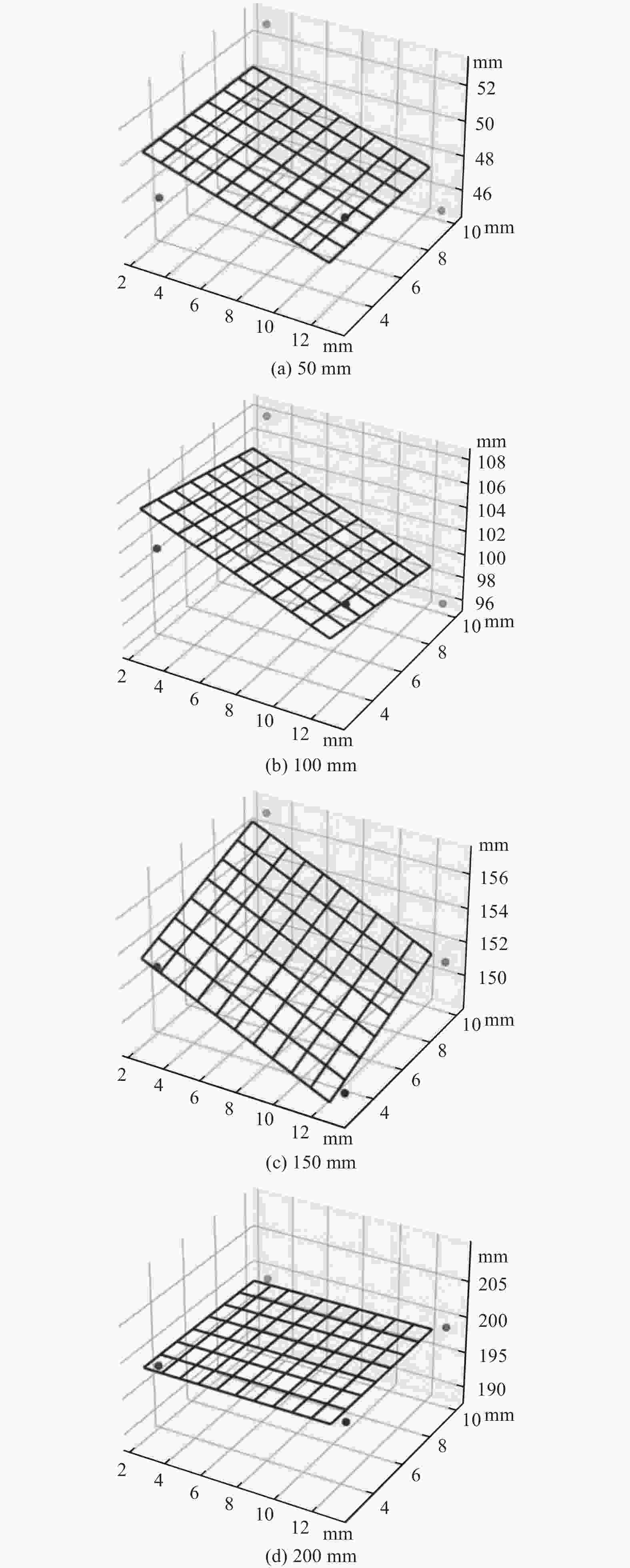
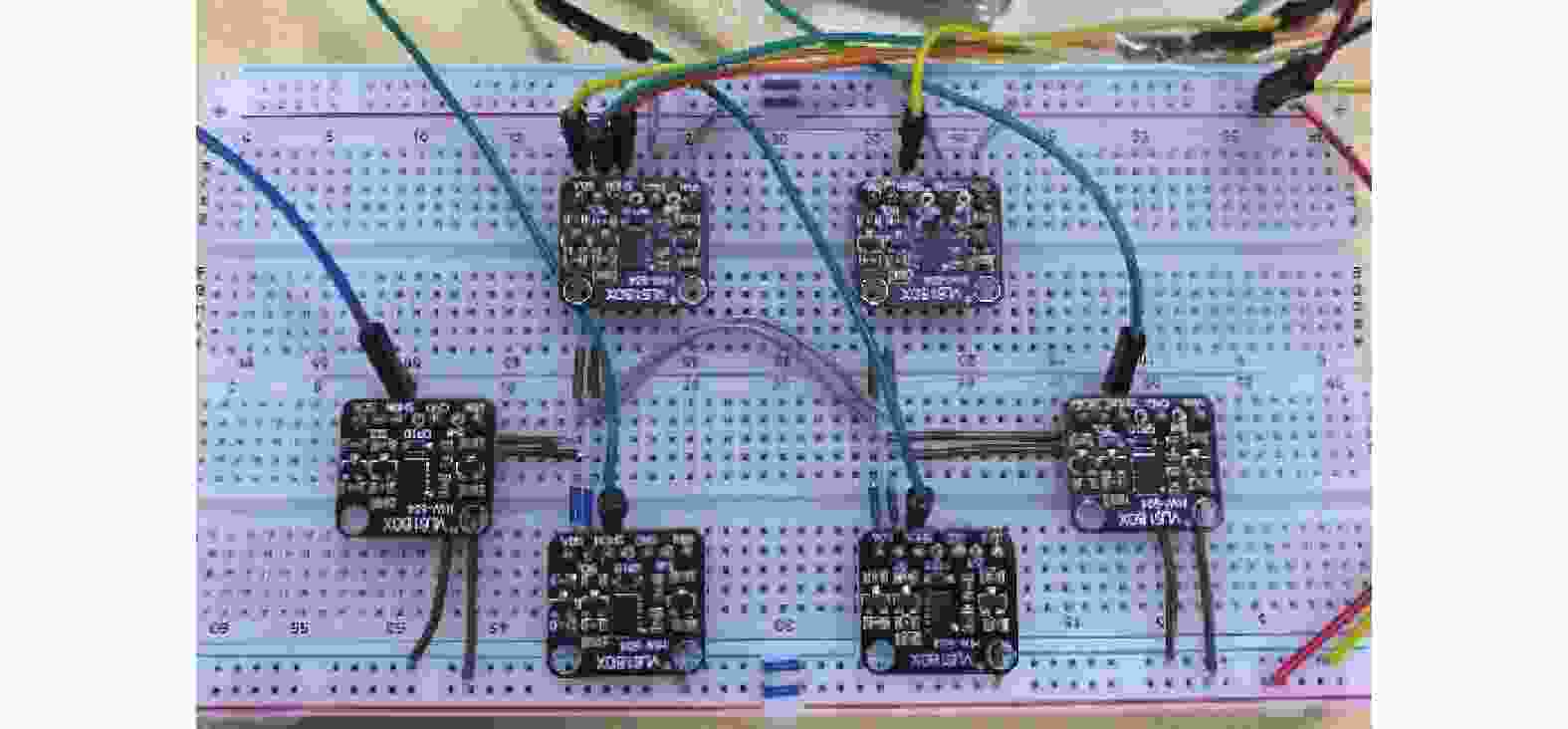
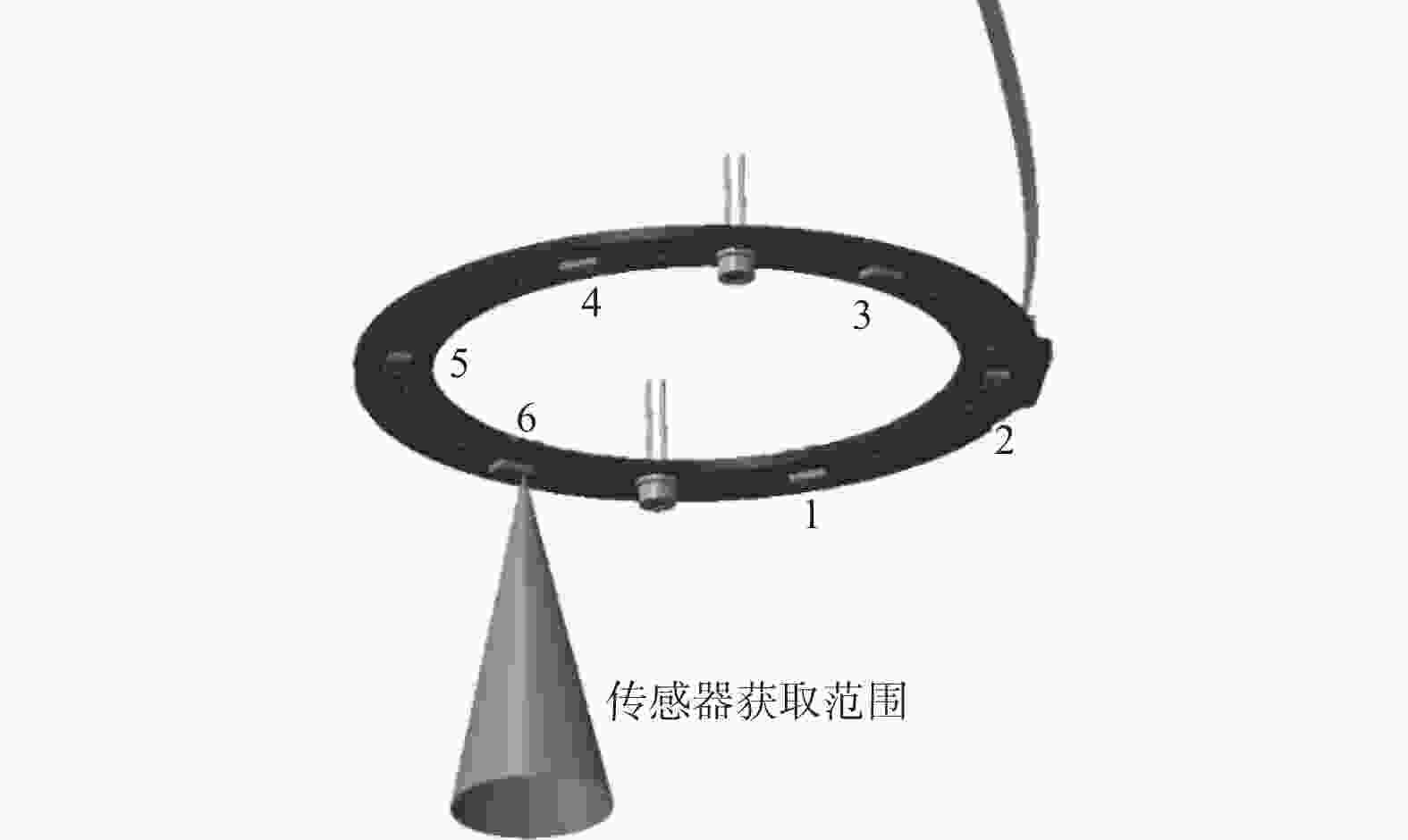
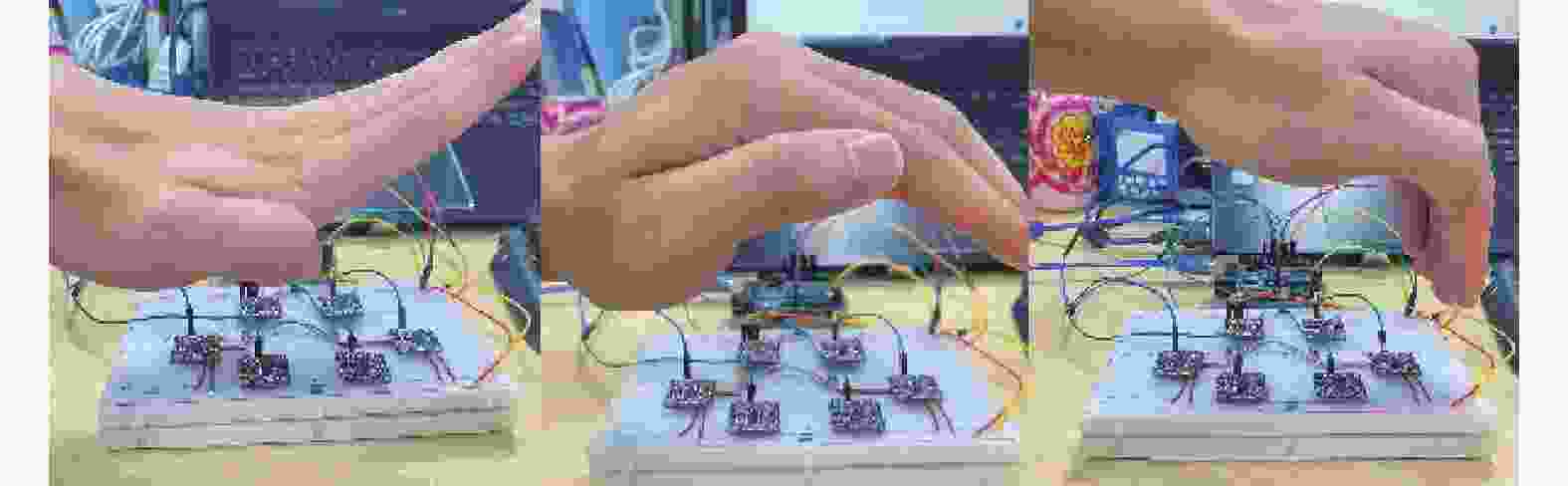
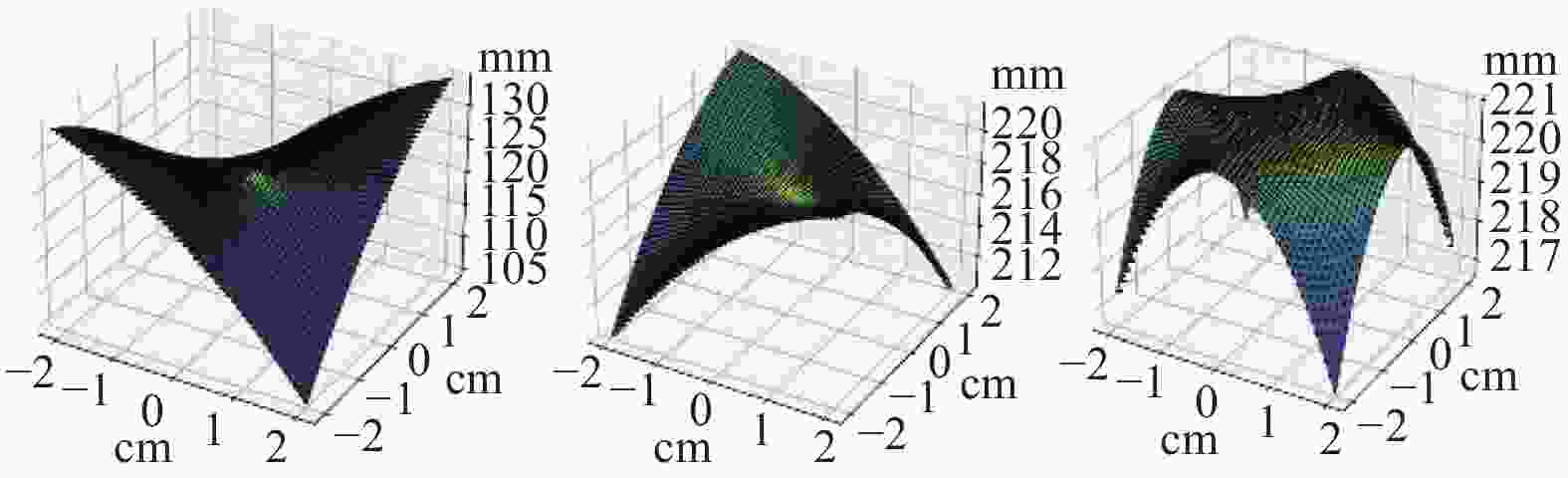
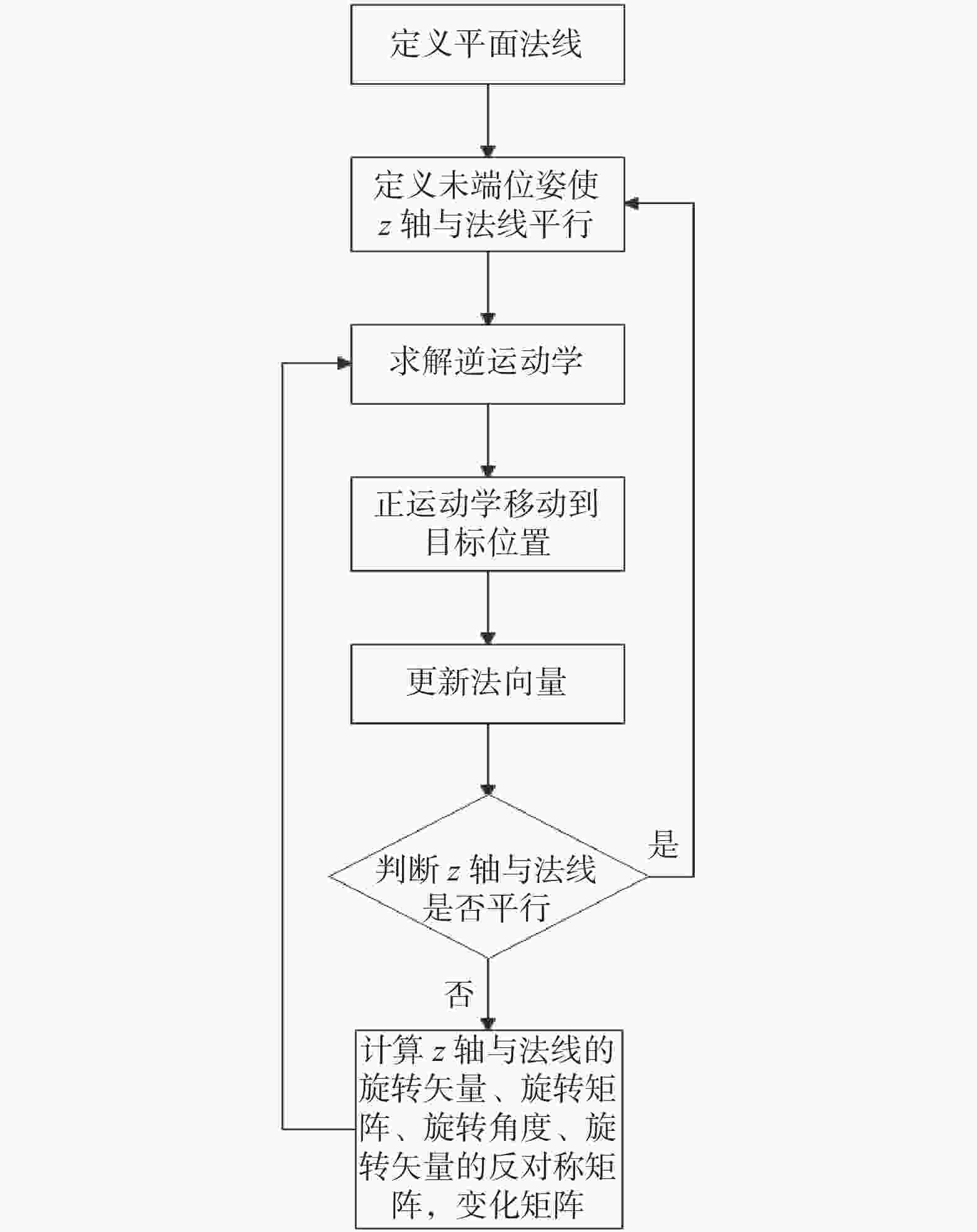
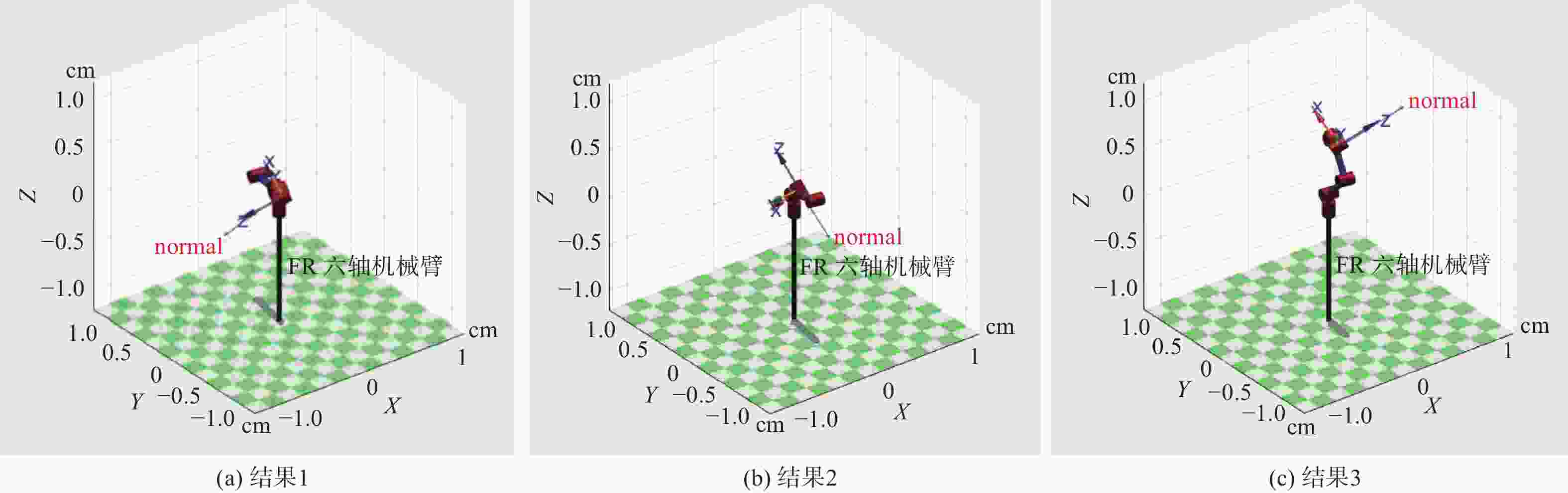
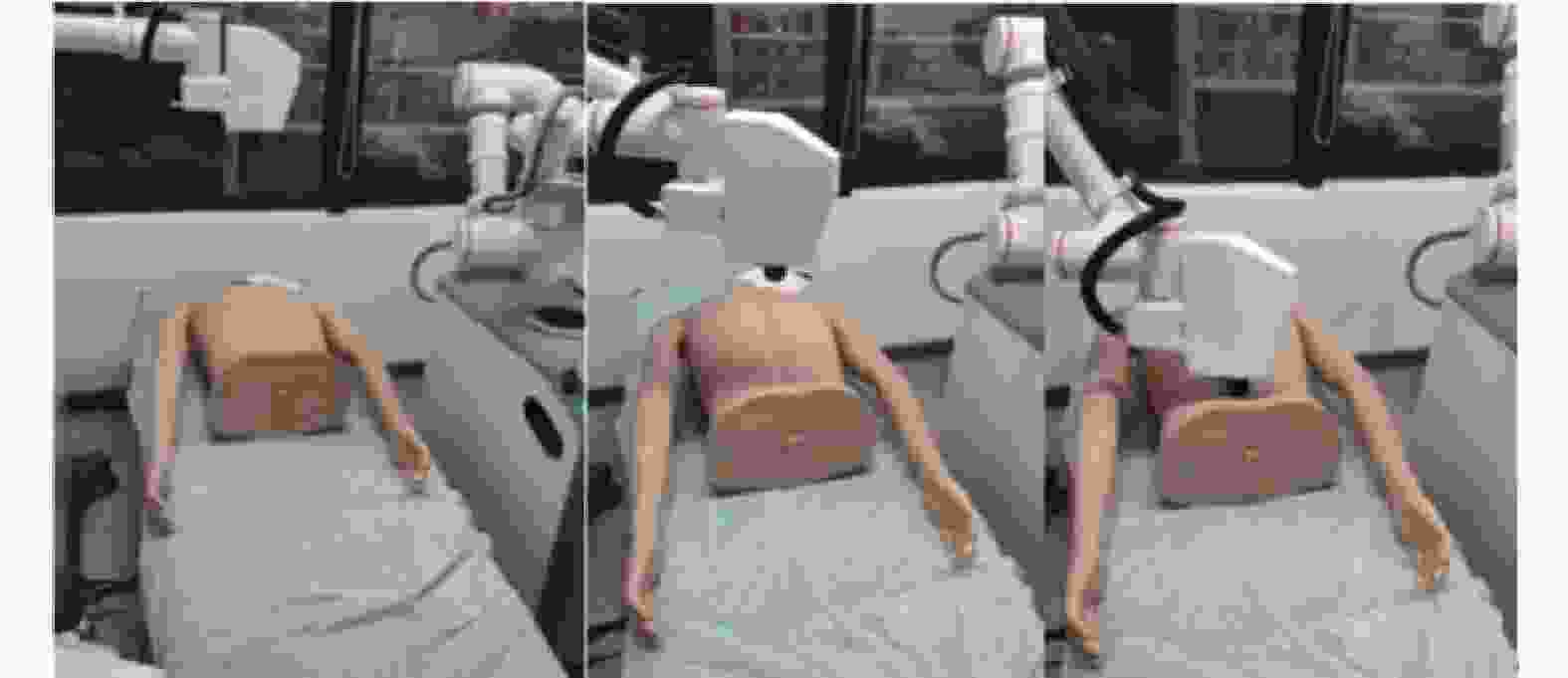
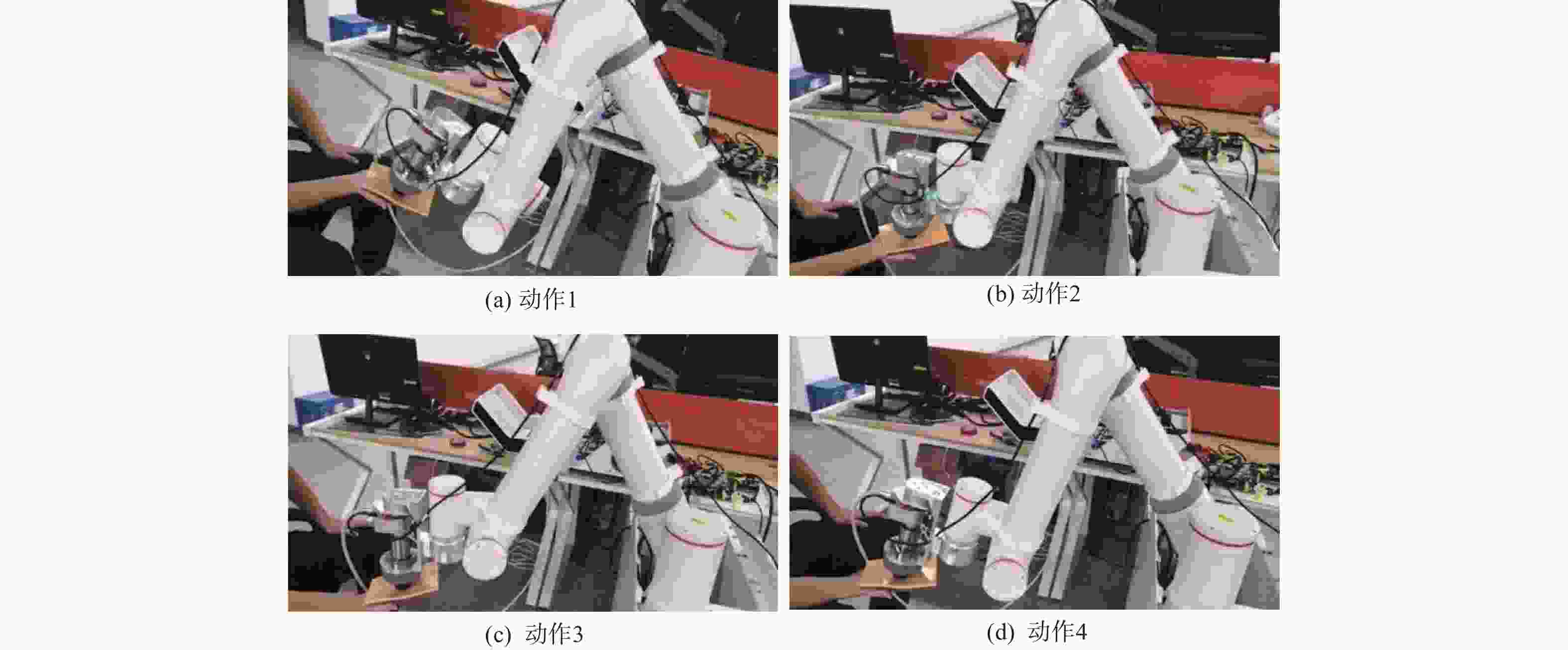
摘要: 在按摩养生服务行业及肌肉拉伤理疗领域,用机械臂代替人工,不仅解放了人力,还能更加系统、精确地控制理疗设备的姿态。冲击波理疗需要与人体表面接触且以一定的姿态工作,如法线方向,而控制机器人的姿态始终从人体面法向进行工作是一大难点。基于飞行时间传感器提出冲击波机器人姿态控制,将多个VL6180X传感器组成测距传感器阵列安装于机械臂末端,测量机器人到人体表面的距离获得人体表面位置信息,根据该信息使用最小二乘法实时构建人体表面模型,控制机器人姿态,从法线方向对人体进行理疗按摩。
-
关键词:
- VL6180X测距传感器阵列 /
- Arduino UNO微控制器 /
- 最小二乘法 /
- 机械臂姿态控制
Abstract: In the service industry involving massage and health preservation, as well as the field of physical therapy for muscle strains, replacing manual labor with robotic arms can not only free up manpower, but also control the posture of physical therapy equipment more systematically and accurately. Shock wave therapy requires contact with the human body surface and operates in a certain posture, such as normal direction, and it is a major difficulty to control the robot posture to work from the normal direction of human body at all the times. The posture control of shock wave robot based on time-of-flight sensors was proposed, ranged sensor array with multiple VL6180X sensors was mounted on the end of the robot arm, and the distance from the robot to the human surface was measured to obtain the human surface position information. Based on this information, a human surface model was constructed in real time using the least squares method to control the robot posture and perform physiotherapy massage on the human body from the normal direction. -
-
[1] 马红霞, 丁薇, 佟河亭. 体外冲击波治疗仪控制系统设计[J] . 青岛大学学报(工程技术版),2020,35(4):77 − 81. [2] 李正义. 机器人与环境间力/位置控制技术研究与应用[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2011. [3] LI S Z. Markov random field modeling in image analysis [M]. Heidelberger: Springer Science & Business Media, 2009. [4] HUANG Z L, WANG X G, WEI Y C, et al. Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation[EB/OL].(2020−07−09)[2022-08-30]. http://arxiv.org/pdf/1811.11721. [5] DAI J F, QI H Z, XIONG Y W, et al. Deformable convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice: IEEE, 2017: 764−773. [6] 郑欣悦, 赖际舟, 吕品, 等. 基于红外视觉/激光雷达融合的目标识别与定位方法[J] . 导航定位与授时,2021,8(3):34 − 41. [7] 王洋, 王俊元, 杜文华, 等. 基于最小平方中值的点云平面拟合算法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展. 2023, 60(4). DOI: 10.3788/LOP213208. [8] 刘梅姜. 基于多项式拟合模型的GPS高程转换方法研究[J] . 福建地质,2012,31(1):84 − 89. [9] 高原, 张恒璟, 赵春江. 多项式曲面模型在GPS高程拟合中的应用[J] . 测绘科学,2011,36(3):179 − 181. [10] 曹湘斌, 颉炯. 基于多传感器数据融合的机器人测距系统设计[J] . 电气传动自动化,2020,42(6):16 − 18. [11] 孙晶. 传感器的原理与应用研究[J]. 科技咨询, 2011(21): 4. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3791.2011.21.004. [12] 樊鹏辉, 杨光永, 程满, 等. 基于线性补偿的测距传感器结构设计与参数优化[J] . 单片机与嵌入式系统应用,2021,21(2):82 − 85. -





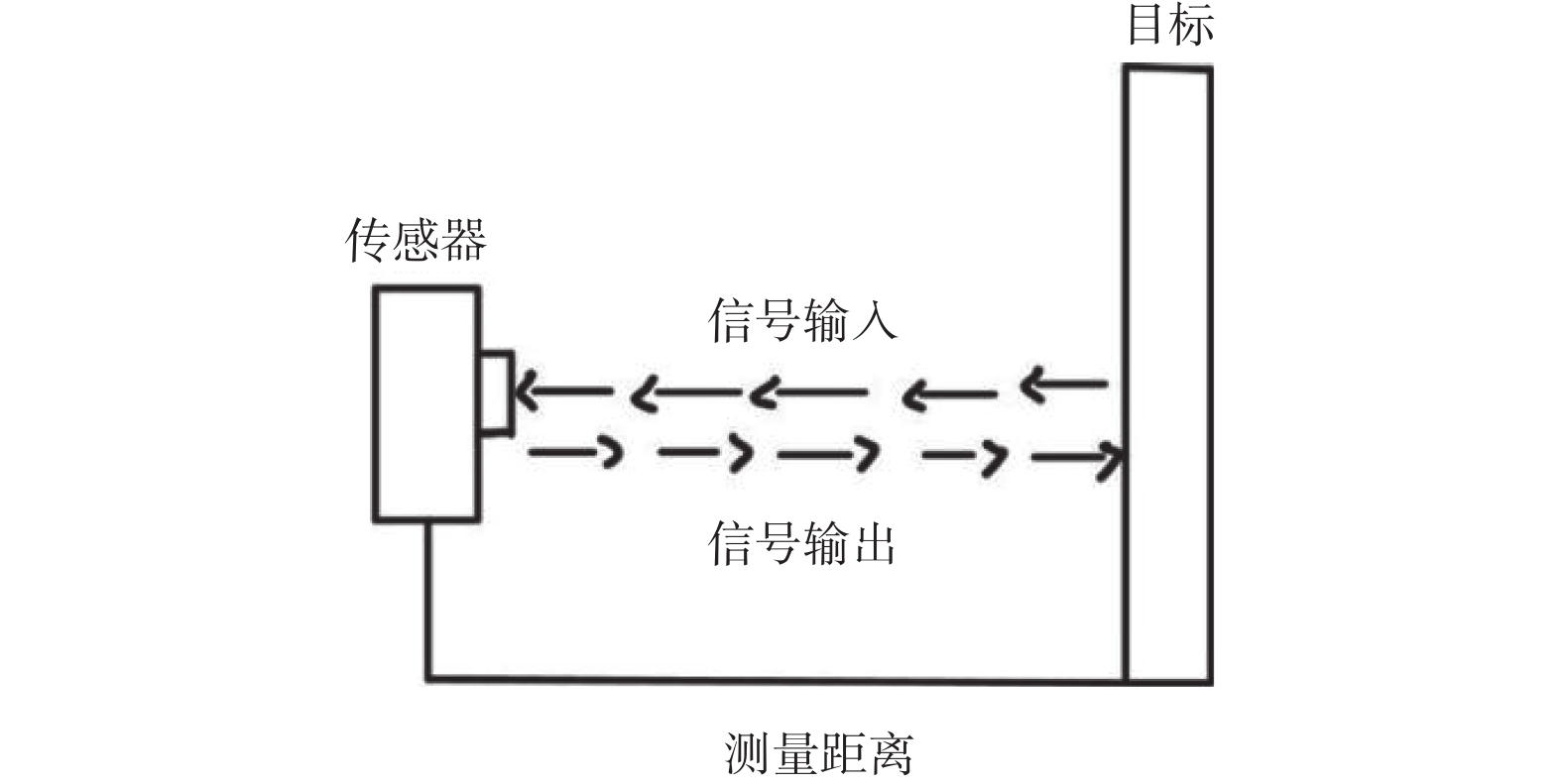
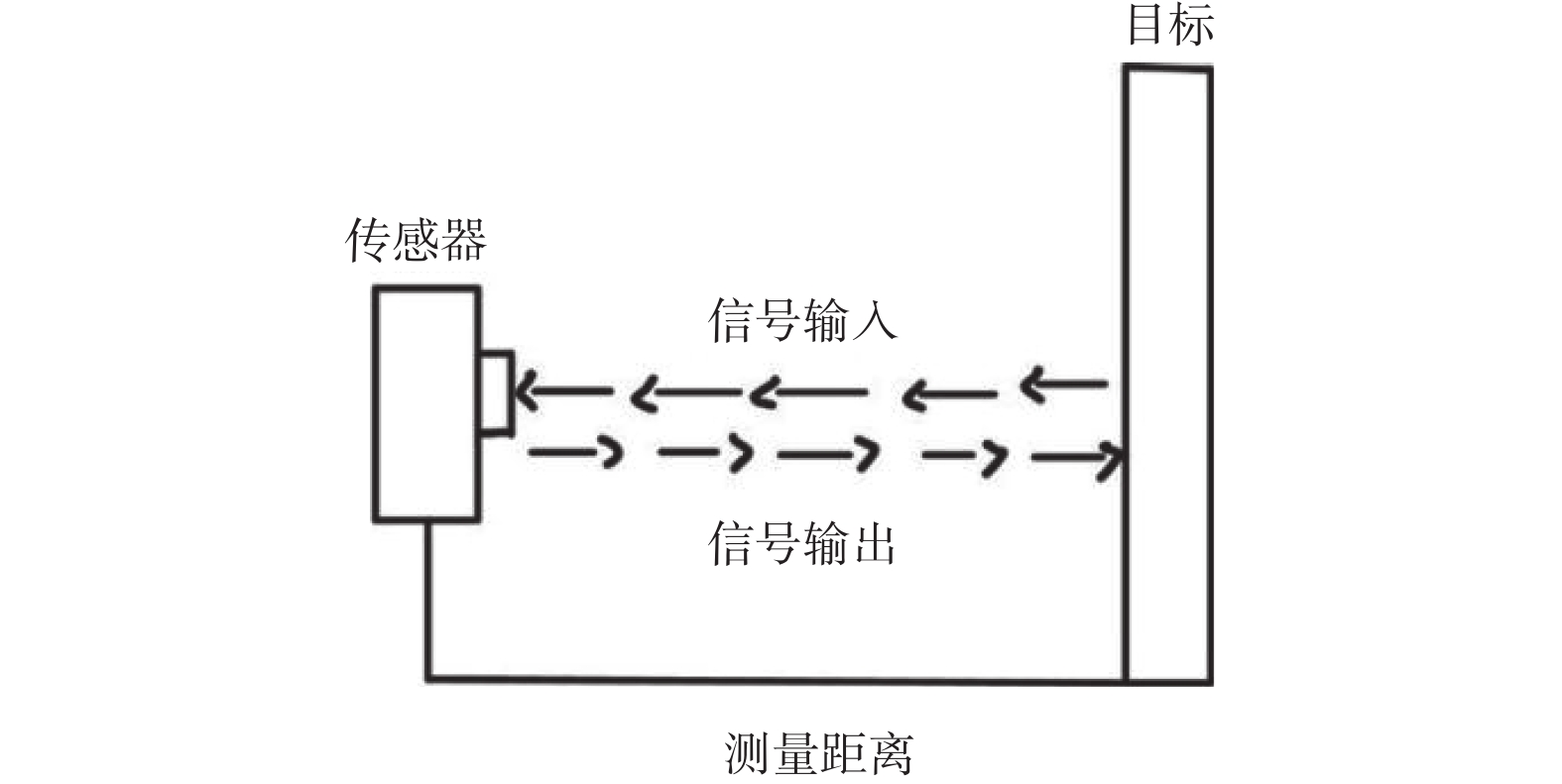
 下载:
下载: